The Product Strategist Role – Responsibilities, Traits, and Career Path
Product strategy is key for business success. This guide will reveal what product strategists do, their essential skills, how they differ from managers, challenges faced, and real examples of effective strategies.

In today's rapidly evolving business world, having a strong product strategy is essential for companies to stay competitive and meet customers' needs.
This is where product strategists come in.
As versatile and vital team members, product strategists leverage creativity, analytical skills, and market understanding to develop successful product roadmaps that align with business objectives.
But what exactly does a product strategist do day-to-day?
What skills and experience are required for the role?
How do they collaborate with other functions like product management?
This article will explore the responsibilities, essential abilities, career pathways, tools, challenges, and more that come with being a product strategist.
We’ll demystify this complex strategic role by providing real-world examples of effective product strategies and clarifying how product strategists differ from product managers.
Most organizations do not have this role, and it appears most often in product organizations with thousands of employees requiring greater coordination.
Whether you are interested in becoming a product strategist or simply want to better understand how they steer products to success, this guide will equip you with a comprehensive look into product strategy.
Here's what you need to know about the role
- The Role
Product Strategists are responsible for crafting long-term product visions and strategies. This involves conducting market research, identifying opportunities, and directing product trajectory to align with business goals. - Skills
Essential skills include strategic thinking, data analysis, communication, and collaboration. These enable strategists to develop innovative ideas, understand customer needs, and work cross-functionally. - Challenges
While Product Strategists focus on the overall long-term product vision and strategy, product managers handle the short-term, day-to-day tasks and execution of individual product development. Strategists develop the roadmap and direction, while managers implement and ensure success of specific products.
The Role of a Product Strategist
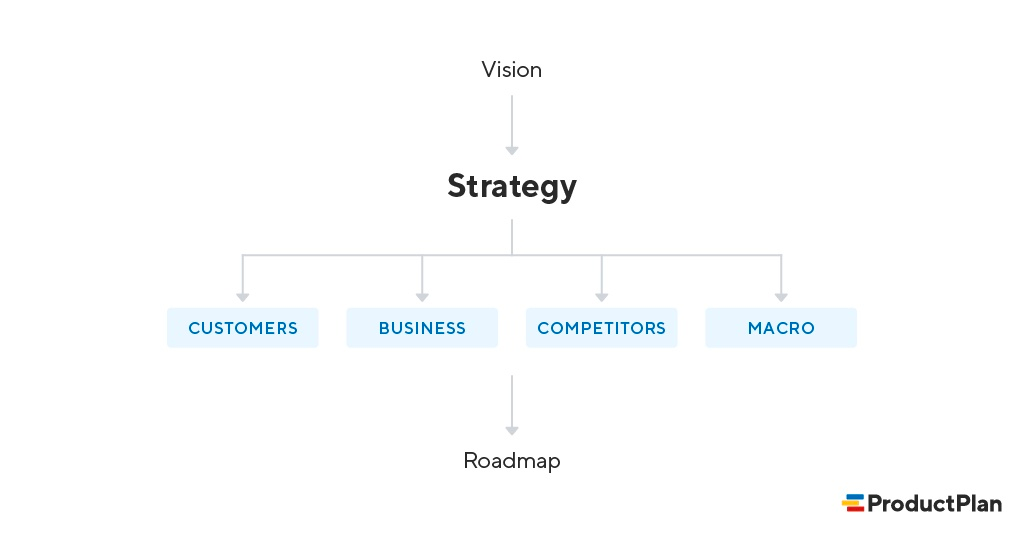
A product strategist is focused on the big picture vision and long-term planning for products. Their core duties include:
Conducting in-depth market research and analysis
- Performing competitive analysis to identify market gaps, opportunities, and threats
- Researching target user pain points, unmet needs, and areas for innovation
- Analyzing performance metrics and trends for the company's current product offerings
Developing long-term product strategy and roadmaps
- Crafting an overarching product vision aligned to business goals
- Mapping out multi-year product roadmaps and lifecycles
- Determining optimal timing and sequencing for new product launches
Identifying partnerships and licensing opportunities
- Researching potential partnerships to extend product reach or capabilities
- Evaluating licensing deals to expand business opportunities
- Assessing strategic alliances to penetrate new markets or user segments
Providing guidance on product positioning and messaging
- Defining compelling and differentiated product positioning
- Developing effective messaging and narratives for marketing campaigns
- Advising on pricing, promotions, and sales strategies
Presenting recommendations and analysis to executives
- Synthesizing research findings and strategy proposals into presentations
- Evangelizing product vision and strategic plans to company leadership
- Gaining buy-in and resources to execute on product strategy
The product strategist role is focused on the big picture thinking required to steer company offerings in the right direction.
Their responsibilities span across research, planning, partnerships, positioning, and executive alignment of the product strategy.
Crafting long-term plans for products, recognizing market opportunities, and directing the product’s overall trajectory are among the key responsibilities of product strategists. Their primary duties revolve around:
- Designing creative solutions
- Validating product concepts
- Modifying solutions
- Examining customer feedback
- Proposing metrics and measures for product advancement
Additionally, they are in charge of constructing the product portfolio and adjusting it to fluctuating market conditions.
A product strategist’s success relies heavily on their ability to think big and creatively, identify opportunities that others may overlook, and plan effective methods of executing ideas while considering market demands. Informed decisions about product positioning, target audience, and market entry strategies are made by product strategists through market research and collaboration with marketing teams.
Working in conjunction with cross-functional teams, including engineering, design, and marketing, product strategists ensure the roadmap is in harmony with the organization’s overall business objectives.
They must possess the following capabilities:
- Strategic thinking
- Problem-solving
- Data analysis
- Market research
- Communication
- Collaboration
These capabilities enable product strategists to generate innovative ideas.
Vision and Strategy Development
Formulating product vision and strategy falls under the responsibility of product strategists. This involves:
- Analyzing market trends
- Identifying customer needs
- Engaging with stakeholders
- Identifying business partnerships to expand the company’s reach
- Assessing the value of new products.
Product strategy aids in comprehending what must be built and the rationale behind it. Northwestern’s Kellogg School of Management offers a product strategy course that provides a comprehensive overview of stakeholders’ needs across various lifecycle stages, assisting product strategists in optimizing their performance and the product.
Collaboration with Cross-Functional Teams
Product strategists work with cross-functional teams, like product managers, engineers, marketers, and sales teams, to put product strategies into action and gather feedback. This collaboration is essential for product strategists to facilitate growth, as it includes assisting with development backlogs, product planning releases, user decision analysis, and presenting ideas to stakeholders.
The significance of collaboration for a product strategist is to:
- Work efficiently with different teams and stakeholders
- Ensure the overall success of the product strategy
- Maintain the harmony of the product roadmap
- Meet the organization’s long-term objectives
Essential Skills for a Successful Product Strategist
Key skills for a successful product strategist include:
- Strategic thinking
- Problem-solving
- Data analysis
- Market research
- Communication
- Collaboration
N26 encourages product strategists to challenge the status quo, demonstrating their entrepreneurial spirit and creativity.
With a strong foundation in the following competencies, a product strategist can excel in their role:
- Data acumen
- Excellent communication abilities
- Market research capabilities
- User experience insight
- Business analysis aptitude
- Analytical prowess
- Technical proficiency
These competencies enable product strategists to devise innovative product ideas and plans that align with market needs and company objectives.
Understanding the product development process and the customer’s needs requires a deep understanding of market research and the ability to analyze data. By honing these key skills, product strategists can create effective strategies that lead to successful products and ultimately pave the way for their career growth.
Strategic Thinking and Problem-Solving
Evaluating a situation, suggesting viable solutions, and making decisions that result in the most beneficial outcome are part of strategic thinking and problem-solving, key skills for product strategists. This process incorporates imaginative thinking, thorough analysis, and the capacity to think unconventionally. Product strategists must be able to recognize opportunities, assess data, and make decisions that will result in the most beneficial outcome for the product.
Examples of strategic thinking and problem-solving include analyzing customer feedback to identify areas of improvement, developing a plan to launch a new product, and creating a strategy to increase customer engagement. However, these skills may present challenges such as managing limited resources, making decisions in a timely manner, and maintaining focus on the goal.
Data Analysis and Market Research
Proficiency in data analysis and market research is required for product strategists to make wise decisions regarding product positioning and potential opportunities. Analytical skills, the ability to dissect complex issues into manageable parts, and the capacity to conduct extensive research are essential for understanding customer needs and performance.
Market research is a vital element that product strategists rely on to:
- Assess product success
- Gain an improved comprehension of customer needs and performance
- Recognize areas for further exploration
- Make judicious decisions about product viability
By mastering data analysis and market research, product strategists can better position themselves to create successful and innovative products.
Communication and Collaboration
Product strategists, who must interact with a variety of people and groups within and beyond the organization, need exceptional communication skills. To be successful, product strategists must be adept at:
- Communicating with stakeholders to ensure that expectations are fulfilled
- Effectively balancing competing interests
- Prioritizing tasks to guarantee the success of the product strategy
Product strategists should be comfortable utilizing the following collaboration tools:
- Chat applications
- Virtual whiteboards
- Video conferencing
- Project management software
By honing their communication and collaboration skills, product strategists can efficiently work with cross-functional teams, driving the successful execution of product strategies and ensuring the overall success of the product.
Product Strategist vs. Product Manager: Understanding the Differences
Though both product strategists and product managers play significant roles in product development, they differ in their responsibilities and focuses. A product strategist takes a broader view to inform the company’s product plans, while a product manager is responsible for the success of individual products. The product strategist is tasked with long-term planning and strategizing for future product lines, while a product manager is responsible for the development and management of a particular product.
In terms of scope and focus, product strategists develop and execute the overall product strategy, including conducting market research, analyzing the competitive landscape, and recognizing new avenues for product development and innovation. Product managers play a critical role in the product development process. They manage day-to-day activities such as prioritizing features, working with the development team, and ensuring timely delivery..
The long-term vision of a product strategist is to create a comprehensive product roadmap that aligns with the organization’s objectives, while the short-term execution responsibilities of a product manager involve implementing the strategy and ensuring product success. By understanding the differences between these roles, organizations can better allocate resources and achieve their product goals.
Scope and Focus
Product strategists focus on the overall product vision and strategy, including conducting market research, analyzing the competitive landscape, and identifying new avenues for product development and innovation. Part of their role is to develop and execute the product strategy in alignment with the organization’s long-term objectives, which is why product strategists spend a significant amount of time on these tasks.
Product managers, on the other hand, handle day-to-day tasks and product development. They are accountable for overseeing the product development cycle. This includes setting priorities for new features, cooperating with the dev team and assuring that deadlines are met. Their primary focus is the success of individual products within the company’s portfolio.
Long-Term Vision vs. Short-Term Execution
Product strategists develop long-term plans and visions for products. They are responsible for constructing the long-term vision and strategy for a product, in addition to supervising the short-term execution of that strategy. This involves identifying market opportunities, creating roadmaps for new product features and enhancements, and ensuring that the product is in line with the organization’s long-term strategy.
Product managers focus on executing these strategies in the short term. This includes implementing the long-term vision and strategy developed by the product strategist, as well as overseeing the short-term implementation of that strategy. By understanding the differences between long-term vision and short-term execution, organizations can better allocate resources and achieve their product goals.
Pathways to Becoming a Product Strategist
Becoming a product strategist can be achieved through several pathways, such as education, professional experience, and certifications. A background in business, marketing, design, or related fields is often required for product strategists, along with a bachelor’s degree or higher education. Higher education can offer product strategists a more comprehensive comprehension of the business and market environment, as well as the abilities and information required to create effective strategies.
Gaining professional experience in product development, management, or related fields can help aspiring product strategists build their skills and knowledge. Professionals can benefit from experience in:
- Product development
- Product management
- Market research
- Data analysis
- Customer experience
This hands-on experience equips them with the relevant skills and knowledge required to thrive in the role, while also providing valuable networking opportunities and potential career advancement.
Certifications and training in product strategy, management, or related areas can further enhance a product strategist’s qualifications and expertise. Examples of such certifications and courses include the MicroMasters in Digital Product Management by Boston University and the Digital Product Management Specialization course. These programs can provide product strategists with valuable qualifications and expertise, setting them up for success in their careers.
Educational Background
A bachelor’s degree in product management, business, economics, or a related field is generally required to become a product strategist. Some positions may also prefer or require a master’s degree in business or a related field. Higher education can offer product strategists a more comprehensive comprehension of the business and market environment, as well as the abilities and information required to create effective strategies.
A strong educational foundation not only equips product strategists with the necessary knowledge and skills but also helps them develop the communication and collaboration skills needed to work effectively with cross-functional teams. Pursuing higher education in relevant fields can greatly enhance a product strategist’s career prospects and success.
Professional Experience
Gaining professional experience in product development, management, or a related field can help aspiring product strategists build their skills and knowledge. This experience is essential for:
- Understanding the product development process, the market, and the customer’s needs
- Developing the skills to effectively collaborate with cross-functional teams
- Making strategic decisions
As professionals gain experience in product development, product management, market research, data analysis, and customer experience, they become better equipped to excel as product strategists. This hands-on experience allows them to apply the concepts they have learned in their education, hone their skills, and build a strong foundation for career growth and success.
Certifications and Training
Obtaining certifications and training in product strategy, management, or related areas can further enhance a product strategist’s qualifications and expertise. Programs such as the MicroMasters in Digital Product Management by Boston University and the Digital Product Management Specialization course provide valuable learning opportunities for professionals looking to expand their knowledge and skills in the field.
By pursuing certifications and training, product strategists can stay updated with the latest industry trends, best practices, and technologies, further bolstering their career prospects and success. These programs can provide them with the knowledge, skills, and qualifications required to excel as product strategists and make a significant impact in their organizations.
Salary Expectations for Product Strategists
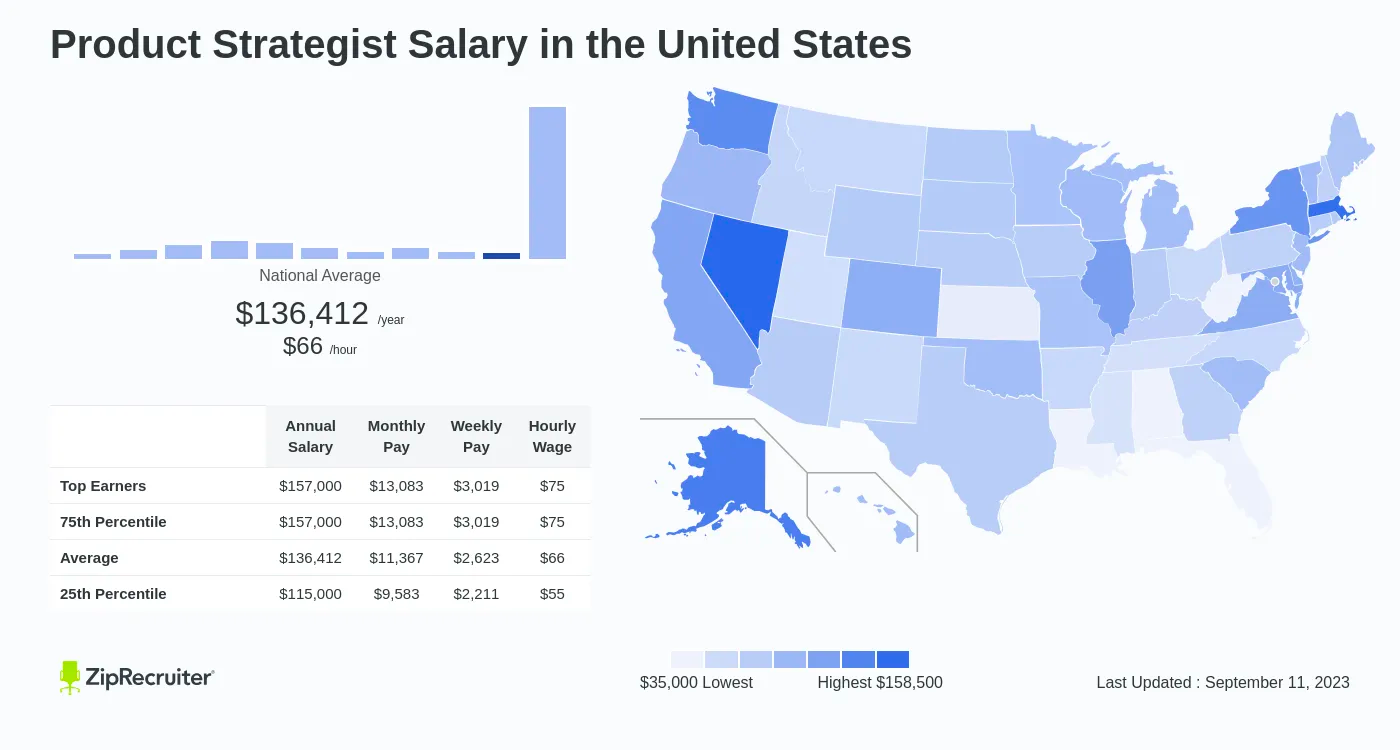
Factors such as industry, location, experience, and company size can cause salary expectations for product strategists to vary. On average, the salary for product strategists is approximately $86,845 in the US. Salaries for product strategists in other countries, such as India and the UK, also vary, with median salaries of approximately 6,00,000 and £44,500, respectively.
To find the most reliable and up-to-date information regarding product strategist salaries, professionals can consult job market reports, salary surveys, and industry-specific resources. By understanding the factors that influence product strategist salaries, professionals can better evaluate job opportunities and make informed decisions about their career paths.
Real-World Examples of Successful Product Strategies
Many real-world examples showcase successful product strategies. One such example is Zoom’s focus on simplicity and user experience, which has led to its rapid growth and adoption. By concentrating on providing a straightforward and user-friendly experience, Zoom managed to stand out in a crowded market and attract a loyal user base.
This example illustrates the power of a well-crafted product strategy that aligns with customer needs and target market trends. By understanding the market and identifying opportunities for innovation and growth, product strategists can create successful strategies that drive product adoption, customer satisfaction, and ultimately, business success.
Challenges Faced by Product Strategists
Challenges faced by product strategists in their roles include staying updated with industry trends, managing stakeholder expectations, and aligning long-term vision with short-term goals. Staying abreast of industry trends is essential for product strategists to persistently have a significant impact in forming successful products that meet the requirements and wishes of customers.
Managing stakeholder expectations can be another challenging aspect of the product strategist role. Product strategists must be adept at:
- Communicating with stakeholders to ensure that expectations are fulfilled
- Effectively balancing competing interests
- Prioritizing tasks to guarantee the success of the product strategy
Reconciling long-term vision with short-term objectives can also be a difficult task for product strategists. They must be able to identify and prioritize tasks that will help achieve the long-term vision while also fulfilling short-term objectives. By addressing these challenges effectively, product strategists can create successful strategies that drive product success and business growth.
Tools and Resources for Product Strategists
Product strategists have a variety of tools and resources at their disposal to help them excel in their roles, including pricing strategy. These include:
- Market research tools such as surveys, focus groups, interviews, and online polls
- Data analysis software like Tableau, Microsoft Excel, and SPSS
- Project management platforms such as Asana, Trello, and Jira
In addition to these tools, product strategists can benefit from professional development courses and certifications, such as the MicroMasters in Digital Product Management by Boston University and the Digital Product Management Specialization course.
By utilizing these tools and resources, product strategists can enhance their skills, stay updated with the latest industry trends, and ultimately, create successful product strategies.
Summary
In conclusion, the role of a product strategist is multifaceted and essential in today's competitive business landscape. By understanding the responsibilities, essential skills, and differences between product strategists and product managers, professionals can better navigate their career paths and make informed decisions.
Whether through education, professional experience, certifications, or a combination of these pathways, aspiring product strategists can equip themselves with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in this dynamic role. With determination, hard work, and the right resources, product strategists can create innovative strategies that drive product success and ultimately, business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is product strategist higher than product manager?
Product strategists and product managers serve complementary roles focused on different responsibilities and scopes. Here is a comparison:
- Scope: Product strategists have a wider scope looking at the full product portfolio and long-term vision. Product managers focus on individual products and near-term execution.
- Responsibilities: Strategists conduct extensive research, develop multi-year roadmaps, and provide guidance on positioning. Managers handle day-to-day product development and launch execution.
- Seniority: The product strategist role is generally more senior to product manager in organizations that have both. However, companies without dedicated strategists rely on senior product managers for strategy.
- Credentials: Strategists are more likely to have advanced education like an MBA. Managers tend to have backgrounds tailored to specific products.
- Salary: According to PayScale, strategists have a higher average salary of $130K vs $85K for product managers. Strategists at the executive level may earn over $200K.
Product strategists focus on high-level strategy while product managers concentrate on tactical execution. Larger companies are more likely to differentiate the roles at different levels, with the strategist being more senior. Smaller organizations may combine responsibilities under senior product managers.
What is the difference between a product manager and a strategist?
Product strategists focus on the overall long-term product vision and strategy, while product managers handle short-term execution and individual product development.
Strategists conduct market research and identify new opportunities, while managers prioritize features and ensure timely delivery. Understanding this difference in scope enables organizations to better allocate resources and achieve product goals.
What does a product strategy analyst do?
A product strategy analyst is responsible for conducting in-depth research and analysis to inform product strategy and planning. Key responsibilities include:
- Reviewing market trends, competitive landscape, and customer usage patterns
- Performing data analysis on product metrics like sales, adoption, and churn
- Building financial models to forecast product performance scenarios
- Identifying new market opportunities and product improvements
- Assessing potential partnerships and licensing deals
- Reviews business development opportunities
- Presenting findings and recommendations to product managers and executives
While product strategists take a broad strategic perspective, analysts focus on researching and modeling specific opportunities. Strong data analysis, financial modeling, and presentation skills are key.
This role conducts analysis of new opportunities to develop sales forecast, builds financial models, tracks customer usage patterns, and makes informed recommendations to product managers
Product strategy analysts support the work of product managers and strategists. Their analytical capabilities help evaluate strategic options and quantify the market potential, costs, and risks associated with new product directions. This information informs strategic planning and decision making.
What is the Role of a Product Strategy Consultant?
A product strategy consultant is an advisor brought in to help companies develop and execute effective product strategies. Their responsibilities include:
- Conducting discovery research to understand the company's business objectives, target users, and competitive landscape
- Performing analysis to identify market opportunities, gaps, and areas for product improvement
- Developing product visions, roadmaps, and go-to-market strategies aligned to the company goals
- Providing recommendations on product positioning, pricing, and marketing
- Coaching teams on implementing data-driven product management disciplines
- Building buy-in for the product strategy across the organization
- Ensuring execution of the strategy through iterative planning and measurement
Product strategy consultants leverage their specialized expertise in business analysis, strategic planning, and product management. They provide an objective outside perspective to shape successful product strategies tailored to the client's specific context. Consultants may advise both early-stage startups still validating product/market fit as well as established companies seeking to expand product lines or revamp stale products. Strong consulting and advisory skills are essential to guide strategic decision making.
What Does a Director of Product Strategy Do?
A Director of Product Strategy is a senior role responsible for overseeing the product strategy function and shaping the strategic direction of a company's entire product portfolio. Key responsibilities include:
- Leading the product strategy team to research market opportunities and develop product roadmaps
- Driving long-term strategic planning and goal setting for the product organization
- Creating business cases and plans to justify strategic initiatives and resources
- Defining processes and best practices for data-driven product management
- Providing guidance to product managers on aligning execution with strategy
- Presenting product strategy recommendations to executive leadership
- Ensuring consistent product messaging and positioning in the market
- Monitoring competitive landscape and industry trends to identify threats and new directions
As the head of product strategy, the director takes a high-level view of the whole product portfolio across multiple lines of business. They guide both product strategy development as well as ongoing alignment of execution to strategic goals. The role requires strong leadership, influencing, and strategic thinking abilities.
