Product Sense Guide
Product teams strive to build successful products, yet often struggle to deeply understand their users. Without grasping the "why" behind customer behavior, product efforts flounder. Read on to unlock the secrets behind building products people love.

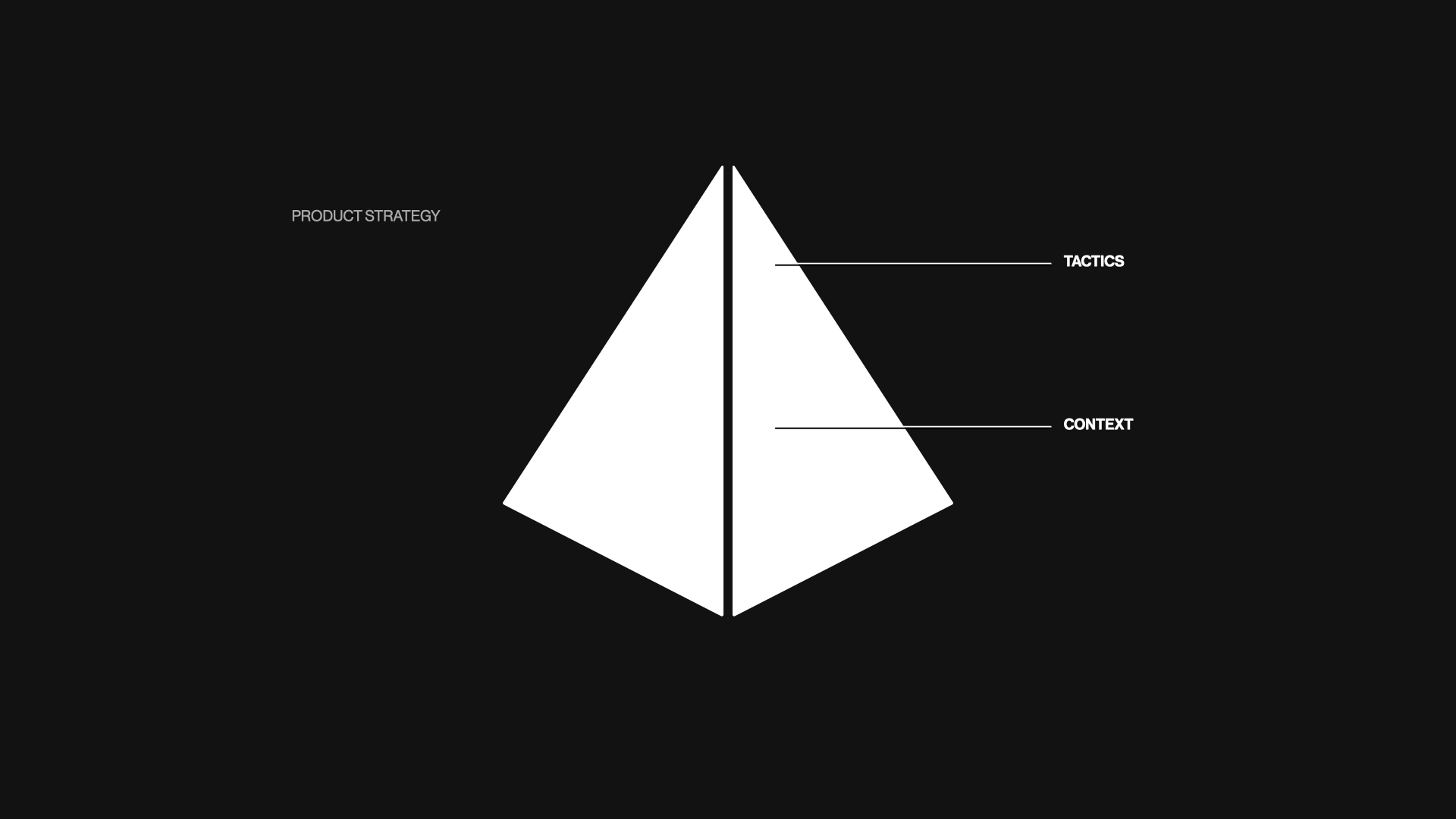
Developing strong product sense is essential for anyone looking to build, market, or invest in successful products. Product sense involves deeply understanding user needs, industry trends, and the competitive landscape in order to identify promising product opportunities. It enables you to think strategically about positioning new and existing products for growth and impact.
This guide will provide frameworks, examples, and exercises to help sharpen your product instincts and insights. With improved product sense, you will be able to spot potential hit products, enhance existing offerings, and bring more value to customers.
Key Takeaways
- Focus obsessively on the user.
The most successful products solve real problems or needs for specific users. Put yourself in the shoes of your target users and design features that directly address their goals and pain points. - Study marketplace trends and competition.
Know what substitute products users have access to and how your product can provide superior value. Be aware of new technologies, regulations, and other industry shifts that present opportunities or threats. - Validate product-market fit.
Make sure there is sufficient market demand for your proposed product before heavily investing in development and launch. Solicit honest feedback from target users early and often. Be ready to iterate if the product is missing the mark.
Let’s begin our journey to mastering product sense.
The Essence of Product Sense
At the core of every successful product manager lies a deep understanding of product sense. It is the ability to create products that seamlessly combine design and functionality while addressing customer requirements and challenges with empathy and curiosity. As Albert Einstein once said, “knowledge is experience, all else is merely information.”
Developing product sense requires:
- Technical knowledge
- Market awareness
- Strategic thinking
- Customer empathy to address user needs and pain points effectively.
Understanding the essence of product sense involves exploring empathy and curiosity’s role and balancing design and functionality, without letting it confuse product sense.
The Role of Empathy and Curiosity
Cultivating empathy and curiosity is vital for product managers in developing product sense. Empathy allows product managers to truly understand customer needs and pain points, while curiosity drives the exploration of innovative ideas and uncovers fresh perspectives on product development.
To cultivate empathy and curiosity, product managers can:
- Empathize with customers to gain insights and deeply comprehend customer requirements and challenges.
- Conduct market research to understand the market landscape and customer preferences.
- Ask thoughtful questions to gather feedback and understand customer needs.
By cultivating empathy and curiosity, product managers can develop a strong product sense and create products that truly meet customer needs.
Curiosity fuels the creative process, leading to creative solutions. It encourages product managers to spend time observing customers, asking key questions, and conducting user testing. This constant pursuit of knowledge and understanding ultimately contributes to developing a strong product sense and the ability to create products that resonate with customers, all while maintaining a fresh perspective.
Balancing Design and Functionality
Striking the right balance between design and functionality is a critical aspect of product sense. Design creates an engaging and memorable user experience, and functionality ensures reliable operation that meets customer needs. To achieve this balance, you can:
- Conduct user research to understand user preferences and pain points
- Test hypotheses through user testing and feedback
- Stay updated with industry trends and best practices
By following these steps, you can create a product that is both visually appealing and highly functional.
Collaboration with cross-functional teams, like designers, developers, and marketers, ensures the product’s visual appeal and functionality. This balance not only results in a product that delights customers, but also contributes to the overall success of the product and the business.
A keen understanding of both design and functionality enables product managers to create standout products that meet customer expectations.
Developing Your Product Sense: Strategies and Techniques
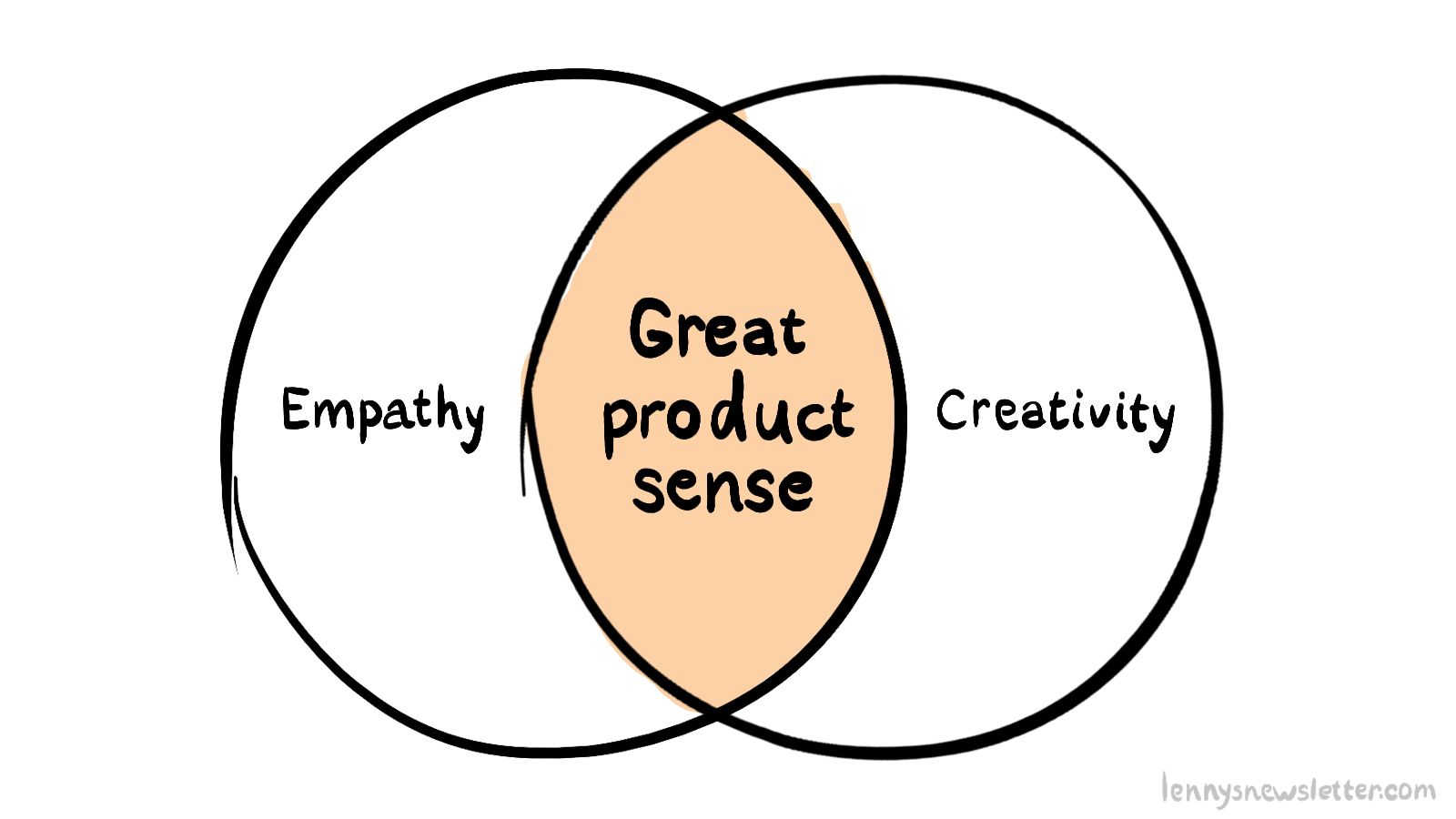
Mastering product sense, although it may seem daunting, is achievable with the right strategies and techniques. Product managers can refine their product sense and make informed decisions through:
- Learning from industry leaders
- Conducting market research
- Gathering user feedback
- Analyzing behavioral data
These strategies not only help in understanding customer needs and preferences, but also contribute to achieving business goals and the overall success of the product and the business.
The following subsections delve deeper into these strategies and techniques, offering practical insights and guidance on developing product sense. From learning from the best to leveraging data and analytics, these approaches will equip you with the tools and knowledge needed to excel in the world of product management.
Learning from Industry Leaders
Observing and learning from successful product managers and industry leaders is an effective way to develop product sense. These individuals have honed their product sense through years of experience, and their insights can provide invaluable guidance for anyone looking to develop their own product sense. Studying their decision-making processes, understanding their problem-solving approaches, and learning from their successes and failures deepens your understanding of excelling in product management.
Besides learning directly from industry leaders, consumption of product management and product sense related content offers diverse perspectives and insights. From articles and blog posts to podcasts and webinars, staying informed on the latest developments and trends in the field can help you stay ahead of the curve and make more informed decisions when it comes to your own products.
Conducting Market Research
Market research, a fundamental tool for developing product sense, aids in understanding customer needs, trends, and competition. Conducting market research enables identification of market gaps, uncovering new opportunities, and gaining insights into target customers’ preferences and behaviors. Various methods can be employed for market research, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, and competitor analysis.
Maintaining up-to-date market knowledge on industry trends is another vital component of conducting market research. Being aware of the latest developments and changes in the market can help you identify potential opportunities and risks, as well as gain insight into customer needs and preferences. Working with cross-functional teams during the research process can also ensure a more comprehensive and effective execution, leading to better product sense and informed decision-making.
User Research and Feedback
User research and feedback are critical to understanding customer pain points and enhancing product sense. Conducting user research, including:
- Observation
- Interviews
- Surveys
- Usability evaluations
Provide product managers with valuable insights into user behavior and preferences. This information can then be used to inform the design and development process, ensuring that the product meets the needs of its users and addresses their pain points.
User feedback is another essential source of information for refining product sense and making informed product decisions. By gathering feedback from customers, product managers can identify areas for improvement, discover new opportunities, and ensure that their product continues to evolve and meet customer expectations.
Through a combination of user research and feedback, product managers can develop a deep understanding of their customers and create products that truly resonate with them.
Behavioral Data and Analytics

Analyzing behavioral data and analytics is a powerful approach for refining product sense and understanding customer preferences. Behavioral data refers to the information generated or collected based on a customer’s interactions and engagement with a business or organization. This data provides valuable insights into customer preferences, interests, and patterns, which can be utilized for decision-making in areas such as marketing, product development, and customer experience optimization.
Analyzing behavioral data and analytics provides product managers with insights into which aspects of their product resonate with customers and identifies areas for improvement. This information can be used to make more informed decisions about product features, design, and functionality, ultimately leading to a better, more successful product.
Building a Strong Product Intuition
Building strong product intuition is a key part of developing product sense. Product intuition is the ability to understand and make meaningful inferences about a product without the need for extensive cognitive analysis or deliberate reasoning. It is often referred to as a sixth sense that product managers develop to make informed decisions and judgments about their products.
The following subsections explore building strong product intuition through drawing inspiration from successful products and testing hypotheses and iterating on ideas. By honing your product intuition, you can make better product decisions, create more successful products, and ultimately, become a more effective product leader.
Drawing Inspiration from Successful Products
Analyzing successful products and understanding their key features serves as a valuable source of inspiration for developing product intuition. By examining the elements that make these products stand out, you can gain insights into what makes a product truly exceptional and apply those learnings to your own product development process.
Some notable examples of successful products include:
- The iPhone
- Coca-Cola
- Google Maps
- Nike’s Air shoes.
- The Rubik’s Cube
These products have achieved considerable popularity and have had a significant impact on their respective markets. By studying these products and understanding the factors that contribute to their success, you can develop a strong product intuition and create products that resonate with customers.
Testing Hypotheses and Iterating
Testing hypotheses and iterating on ideas are also critical to refining product sense and building strong product intuition. Hypothesis testing involves evaluating assumptions about a product or service and pinpointing areas for improvement. By conducting hypothesis testing, product teams can gain a better understanding of user behavior and preferences, which can then be leveraged to refine product sense and make more informed product decisions.
Iterating on ideas is equally important, as it allows product teams to continuously improve their products and adapt to changing customer needs and preferences. By testing hypotheses and iterating on ideas, product managers can refine their product sense and create products that not only meet customer expectations but also stand out in the market.
Leveraging Domain Knowledge and Market Insights
Taking advantage of domain knowledge and market insights is key to developing product sense. By staying informed on industry trends and collaborating with cross-functional teams, product managers can gain a comprehensive understanding of their customers and the market, which can be used to make informed decisions and create successful products.
The following subsections delve into the importance of staying informed on industry trends and the benefits of collaborating with cross-functional teams. By leveraging domain knowledge and market insights, product managers can develop a deep understanding of their customers and create products that truly resonate with them.
Staying Informed on Industry Trends
Staying current with industry trends and news is vital for developing product sense and making informed decisions. By staying informed on the latest developments and changes in the market, you can identify potential opportunities and risks, as well as gain insight into customer needs and preferences, which helps you better understand your target audience.
Various methods can be employed to stay informed on industry trends, such as:
- Reading industry publications
- Attending conferences and seminars
- Networking with professionals in the field
- Using social media to stay informed on the latest news and developments in the industry
These methods can help you stay ahead of the curve and make more informed decisions when it comes to your own products.
Collaborating with Cross-Functional Teams
Collaboration with cross-functional teams offers diverse perspectives and insights, contributing to improved product sense. Cross-functional teams comprise individuals with different areas of expertise, such as designers, developers, and marketers, who can offer valuable insights and ideas for product development.
Collaboration with cross-functional teams ensures the product.
- Meets customer requirements
- Operates reliably
- Facilitates the identification of potential issues at an early stage
- Decreases the time needed for development
- Guarantees that the product meets customer requirements
By fostering a collaborative environment and working closely with cross-functional teams, product managers can develop a deep understanding of their customers and create products that truly resonate with them.
Sense & Respond: developing product sense with quantitative and qualitative signals
There are many ways to develop product sense include: reading about and studying different products, talking to customers and other stakeholders, attending product meetings, and experimenting with different products. Additionally, it is important to be able to think critically and creatively, and to be able to effectively communicate with others.
The frameworks that product managers can use to develop product sense will vary depending on the specific products and markets they are working in. However, some common frameworks that product managers can use to develop product sense include both quantitative and qualitative measures.
Quantitative
- North Star Metric Framework – A north star metric is a business metric that helps teams to identify their goals and track their progress towards reaching them.
- Market Research and Surveys – Market research through surveys generates quantitative attitudinal data that helps with market segmentation and validating customer discovery at scale.
- A/B testing – A/B testing allows for informed decisions to be made about which product features or design elements are more effective and should be included in the final product.
- Product Analytics – Product analytics visualize how how your product is used, what features are used compared to others, and the habits of users.
Qualitative
- The Jobs-to-be-Done (JTBD) Framework – JTBD is a tool that can help determine why customers buy a product, or what they hope to achieve with your product, which can help differentiate your product from that of competitors.
- Competitor Analysis and Benchmarking – Competitive analysis is the process of identifying and evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.Benchmarking is the process of comparing your company's performance against other companies in your industry.
- Customer Discovery – Customer discovery is a process in which startups assess whether there is a market for their product or service by talking to potential customers.
- Product Feedback – Customer feedback is important for product strategy because it helps businesses understand what customers want and need from their products, how well their products are performing, and identify areas for improvement.
North Star Metric
A north star metric is a business metric that is both important and unambiguous. It is a metric that management can use to make decisions and track progress.
A north star metric is a metric that teams can use to measure their progress and performance. It can help teams to identify their goals and track their progress towards reaching them.

Input Metrics
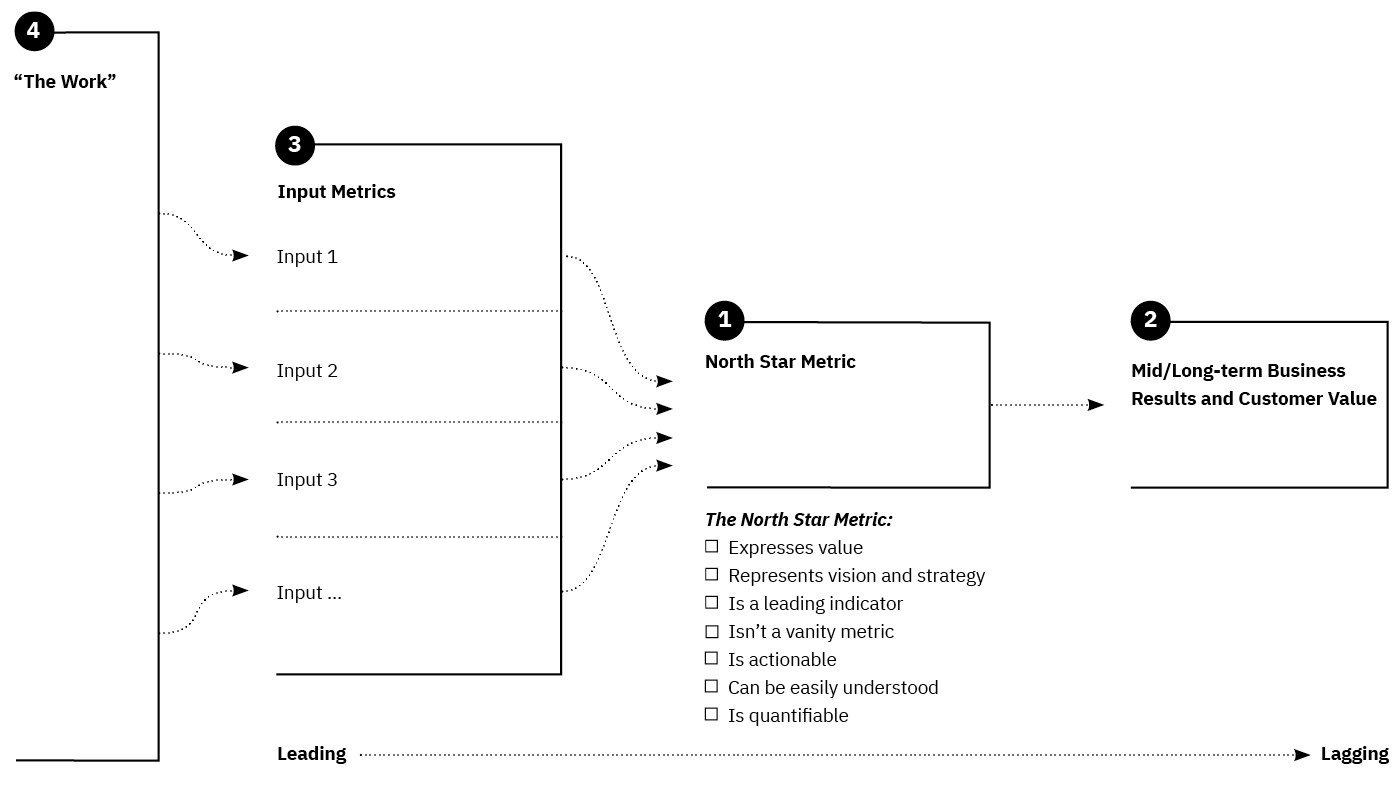
Input metrics are the performance data that are collected and used as the basis for making decisions about where and how to improve the performance of a process or larger metric.
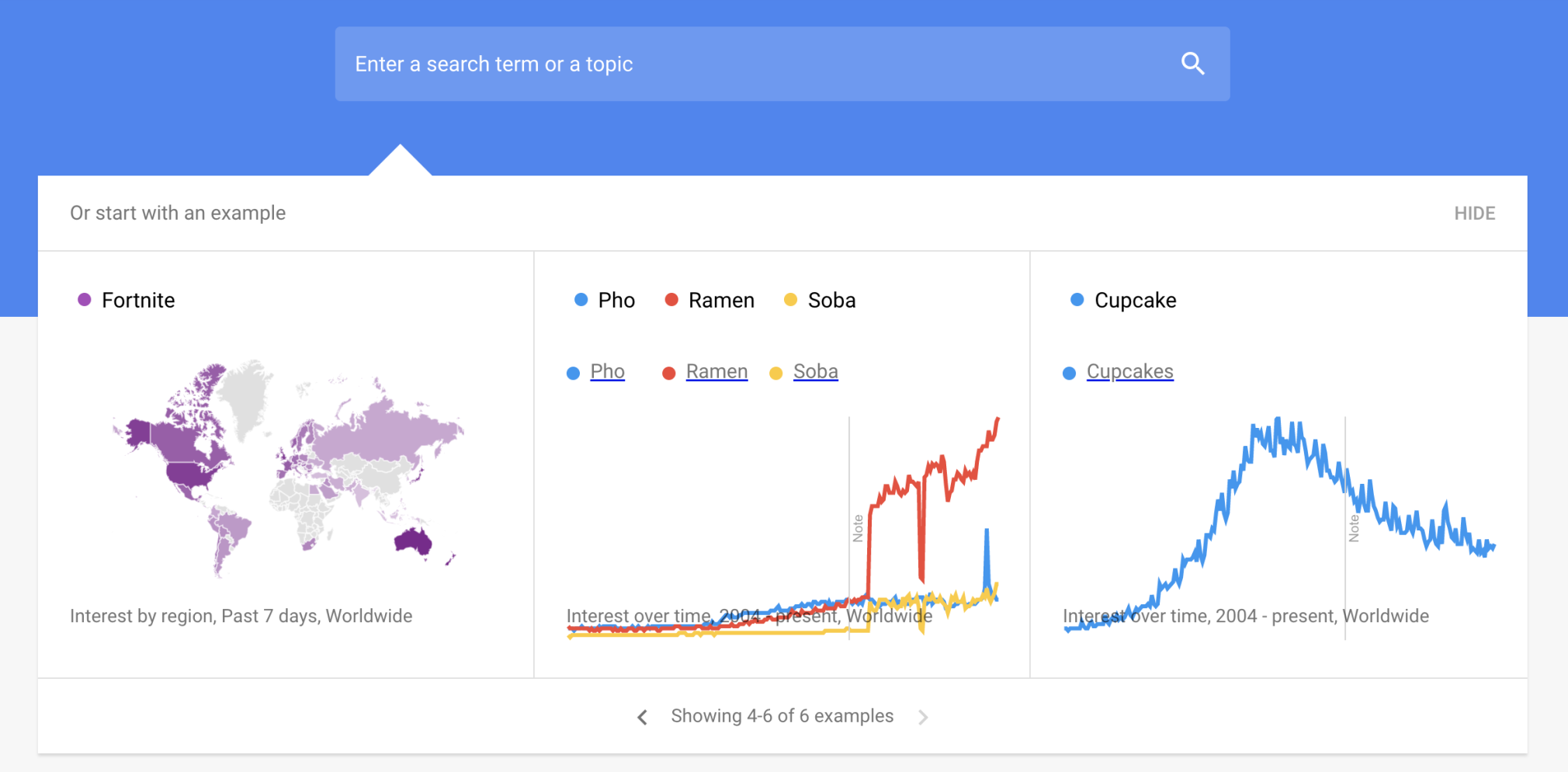
Market Research & Surveys
There are three major types of surveys, each with their own best practices: map-making, intercept, and validation. Survey questions should be designed to generate quantitative data, and surveys should be sent to a representative sample of the target audience to avoid bias.
Map-making surveys are broad, extensive surveys that help build a map of customer attitudes, frequently used for market sizing and validating customer interview insights at scale. Intercept surveys are targeted surveys looking to understand specific attitudes with specific aspects of a product. They are used for things like customer satisfaction or CSAT surveys. Validation surveys are a specific set of mostly standardized surveys that validate value or satisfaction. They include NPS surveys, CES surveys, and others.
Product Adoption & Engagement
There are a few reasons why measuring product adoption and engagement is important. One reason is that it can help you determine whether or not your product is meeting customer needs. If adoption and engagement are low, it may indicate that there is something wrong with your product that needs to be fixed.
Additionally, measuring adoption and engagement can help you understand how your customers are using your product, what features they are using, and how they are interacting with your product. This information can help you improve your product and make sure that it is meeting customer needs.
Poor product adoption means that a product is not being used as much as the company or its creators had hoped. This can be due to a variety of reasons, such as a lack of interest in the product, a lack of awareness of the product, or a lack of understanding of how to use the product.
Poor product engagement means that customers are not using your product as much as you would like them to. This could be due to a number of reasons, such as a lack of features, a confusing user interface, or a lack of marketing and outreach.
The success of a product's revenue model correlates with its users' depth of engagement. A product with good retention (breadth) but without depth of engagement will not become a big business.
Product Retention
Retention and engagement are two sides of the same coin - without one, the other cannot exist. Retention is the number of customers you have at a given time period, while engagement is the depth and intensity of their relationship with your company.
Retention and engagement are both important for different reasons - retention is key to growth, while engagement is key to profitability. Engagement deepens over time as customers learn the product and become more invested in it. The deeper the engagement, the higher the switching costs for customers, which makes it more difficult for them to leave. Engagement builds defensibility by increasing switching costs and making it more difficult for competitors to steal customers.
Product retention is the percentage of customers that continue to use a product or service over a given period of time. It is typically measured by asking customers how often they have used a product or service in the past day, week, or month.
Product retention is important because it is one of the most important factors in a company's success. It is much easier and less expensive to keep a customer than it is to find a new one.
Retention is one of the most important, yet least understood, drivers of growth. It can take years to see its impact on your company’s growth, so it often is deprioritized. However, it’s critical to take a longer term view on growth in order to understand how retention impacts your product. With a longer term view, it’s clear that retention is a key factor in winning the growth race. Companies with higher retention rates will have a significant advantage over those with lower retention rates.
Defining retention incorrectly can lead to inaccurately measuring retention, which can kill your product. Choosing the wrong unit of measurement is a common mistake companies make when measuring retention. Retention should be measured in terms of usage, not revenue.
Retention should be measured on the right frequency to get an accurate understanding of a product's retention. Measuring retention on the wrong frequency can trick you into thinking your product has good retention when it really doesn't. For most B2C social products, engagement should be daily, not weekly or monthly.
Retention metrics can be useful, but they can also be misleading if you don't understand how they work. Breadth of engagement is the percentage of users who are still active in a given time period. Depth of engagement is the strongest indicator of long term-value for both the user and the company. Retention without engagement tells only half the story.

Retention Marketing Strategies
There are many different marketing techniques that can be used in order for companies to keep in touch with their customers and encourage them to return and make another purchase. Retention marketing typically consists of communicating directly with existing customers via email, social media, or a phone call to inform them of product updates and improvements.
Data & Anecdotes
When metrics tell a different story than customers, the company should investigate the discrepancy. The company may find that the metrics are inaccurate or that customer feedback is not representative of all customers. Alternatively, the company may find that it is not meeting customer needs in some way that the metrics do not capture. In any case, discrepancies between customer feedback and metrics should be investigated and addressed.
The thing I have noticed is when the anecdotes and the data disagree, the anecdotes are usually right. There's something wrong with the way you are measuring it. – Jeff Bezos
Customer Feedback
Customer feedback is crucial for product strategy because it allows businesses to understand what customers want and need from their products. This feedback can then be used to improve or create new products that meet customer needs. Additionally, customer feedback can help businesses understand how well their products are performing and identify areas for improvement.
Customer experience is an important aspect of product strategy because it impacts how customers perceive a product. Positive experiences with the product can create loyal customers who are likely to continue using or buying the product in the future. On the other hand, negative interactions will lead customers to seek out alternative products and discourage them from coming back.
A positive customer experience can create loyal customers who are likely to continue using or buying the product in the future. On the other hand, negative interactions will lead customers to seek out alternative products and discourage them from coming back.
In order to make improvements, businesses must understand how customers feel about their product and what they want from it – this is why customer feedback is crucial for product strategy.

Sales Conversations
Sales conversations are important for product strategy because they can help identify what features and benefits are most important to customers and how the product can be improved to better meet customer needs.
Sales conversations can help identify product gaps by giving you an idea of what features and functionality your customers would like to see in your product. This information can help you prioritize product development and determine where to focus your resources. Additionally, sales conversations can help you understand which features are most important to your customers and how they are using your product. This information can help you make decisions about future product development and marketing initiatives.
The sales team is often the first touchpoint a customer has with your product, and can be a valuable source of insight into what drives satisfaction or dissatisfaction with a product. By talking to sales reps regularly you can learn about common pain points and challenges that customers are having as well as their overall experience interacting with the product.
Customer Success
Customer success managers can inform product strategy by sharing customer feedback about what features and functionality they need and value, and what aspects of the product are causing them difficulty or frustration. They can also help identify opportunities for product enhancements or new features that would improve the customer experience and drive greater customer adoption and engagement.
There are a few things that customer success managers can do in order to help account expansion. They can help identify new potential accounts and work with sales teams to target and pursue them. They can also work with current accounts to identify opportunities for growth, and help to develop a plan to expand the account. Additionally, customer success managers can track customer engagement and usage data in order to identify opportunities for up to-scale account expansion.

Jobs to be done
Jobs To Be Done (or JTBD) is a tool that can be used for product strategy by helping to understand what needs a product fulfills for the customer.
Jobs are not solutions to problems. A problem is a gap between the current state and the desired state where there are clear steps for how to resolve the issue. A job has no conditions, but instead describes what results should be accomplished. The reason using JTBD can help product strategy is that it helps determine why customers buy your product, or what they hope to achieve with your product.
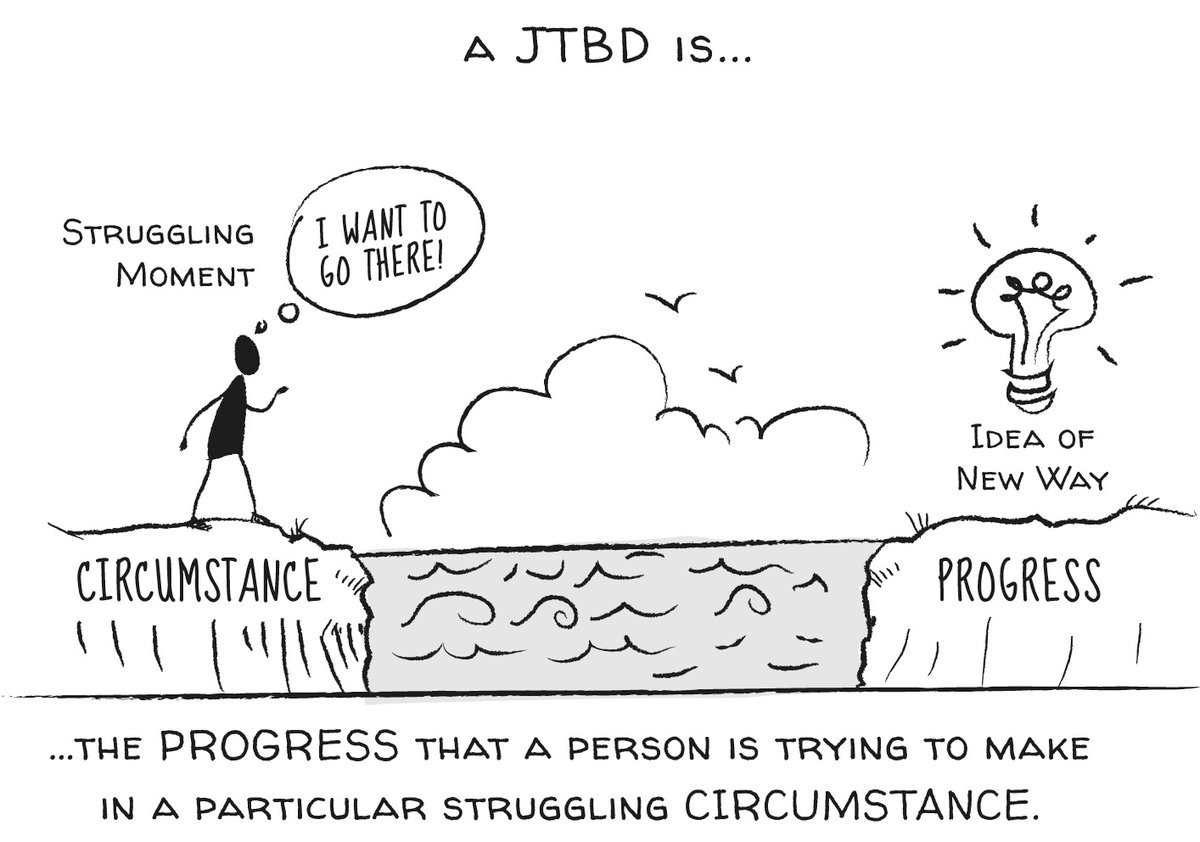
This is a crucial distinction, as solving problems often involves creating a product that has features and benefits that overlap with other products on the market. When this happens, there's no competitive advantage as the new product may only be slightly different from its competitors. In contrast, jobs can help identify why customers buy a product and what they hope to accomplish with it.
This can help differentiate your product from that of competitors, as you will be able to offer features and benefits that meet the specific needs of customers.
The "Why" Behind JTBD
Understanding why people would want to hire a given solution helps identify what makes a product truly unique. Understanding JTBD is about understanding the motives behind what people do. By gaining this knowledge, you'll be able to shape your product strategy into something that aligns with the underlying motivations of customers.
Building Strategy With JTBD
As stated earlier, knowing why people employ a product can help bring insight into the needs and wants of customers. This information can then be used as part of product strategy by helping to create features and benefits that meet customer's jobs to be done. There are several steps in using jobs to inform product design:
- List consumer goals – People perform tasks differently depending on their goals at any given point in time. When creating personas it can be helpful to list each persona's primary goals and then list the tasks necessary to accomplish these goals.
- Analyze your product – Once you've mapped out how different personas perform their job-to-be-done, it's important to closely analyze your product and its features. Identify which products or features perform better than others and determine why this is the case. Look for patterns in usage that may indicate underlying motivations of customers.
- Create a set of design principles – When using JTBD in product strategy, it can be helpful to create a set of design principles based on what you've learned about customer motivations behind jobs to be done . These principles should inform new feature development as they are based on customer needs that are already part of the product offering. This helps ensure that new features are in line with the original intent of the product and that users will be able to easily accomplish what they want.
As a quick reminder, JTBD is focused on helping to understand why customers purchase a particular product or use a given feature. This information can help support product strategy by providing insights into customer needs from which new features can be developed. By using this perspective, you'll gain deeper customer insight and differentiate your product from competitors.

CSAT and PMF Surveys
Two valuable customer surveys include Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Product-Market Fit (PMF) surveys. These surveys can be especially important for identifying opportunities to create new features or provide additional functionality that may improve the customer experience.

CSAT
CSAT can be used to inform product strategy by understanding what features are important to customers and what needs to be improved. Additionally, CSAT can be used to track customer satisfaction over time to ensure that products are meeting customer expectations.
PMF
A PMF survey can help inform product strategy by providing insights into what potential or current customers find valuable in a product. This information can help inform decisions about what features to prioritize in future product iterations. Additionally, the survey can provide insights into customer satisfaction and potential areas for improvement.
The Path to Becoming a Product Leader
Becoming a product leader involves more than developing product sense; it necessitates cultivating a growth mindset, building a diverse skill set, and teaching others product sense. Product leaders not only excel in creating successful products, but they also inspire and guide their teams, fostering a culture of creativity and collaboration within the organization.
The following subsections discuss the importance of cultivating a growth mindset, building a diverse skill set, and teaching others product sense. By mastering these skills and abilities, you can embark on the path to becoming a product leader and make a lasting impact on your organization and the world of product management.
Cultivating a Growth Mindset
A growth mindset is vital for continuous learning and improvement in product sense. It is the belief that intelligence, abilities, and talents can be cultivated and enhanced through effort and learning. Individuals with a growth mindset are invigorated by challenges and perceive them as opportunities for growth and improvement, rather than setbacks.
Developing a growth mindset involves setting challenging goals, welcoming failure as a learning opportunity, and seeking feedback from others. By fostering a growth mindset, product managers can remain open to new ideas, take calculated risks, and learn from their mistakes. This mindset not only contributes to the development of product sense, but also allows product managers to excel in their careers and become effective product leaders.
Building a Diverse Skill Set
Developing a diverse skill set, encompassing technical, strategic, and customer empathy skills, aids in becoming a product leader. A diverse skill set enables product managers to approach problem-solving from various perspectives, leading to more innovative solutions and better decision-making.
In addition to technical skills, such as data analysis and software development, product managers should also focus on developing strategic thinking and decision-making abilities, as well as customer empathy skills. By cultivating a diverse skill set, product managers can not only develop their product sense, but also become effective product leaders capable of guiding their teams and creating groundbreaking solutions.
Teaching Others Product Sense
Improving product sense to others is a vital step towards becoming a product leader. By sharing their knowledge and expertise with others, product managers can reinforce their own understanding of product sense and contribute to the growth of the product management community.
Imparting product sense to others involves helping them comprehend the elements that make a product exceptional, such as understanding user needs, staying informed on market trends, and focusing on details. Teaching product sense not only strengthens one’s own knowledge, but also fosters a culture of creativity and collaboration within the organization, ultimately leading to the development of successful products and effective product leaders.
Four-bullet Summary
- When metrics tell a different story than customers, the company should investigate the discrepancy.
- Product adoption and engagement are important because they can help you understand whether or not your product is meeting customer needs. Retention is key to growth, while engagement is key to profitability.
- Understanding JTBD is about understanding the motives behind what people do. By understanding why people would want to hire a given solution, you can identify what makes a product truly unique.
- Customer success managers can inform product strategy by sharing customer feedback about what features and functionality they need and value, and what aspects of the product are causing them difficulty or frustration. They can also help identify opportunities for product enhancements or new features that would improve the customer experience and drive greater customer adoption and engagement.
Recommended Reading