A Guide to Product Management: Essential Skills, Responsibilities, and Tools
From inception to launch, product managers steer the direction of products to meet customer needs. Mastering the key components of product management and honing essential skills pave the pathway to success in this multifaceted role.
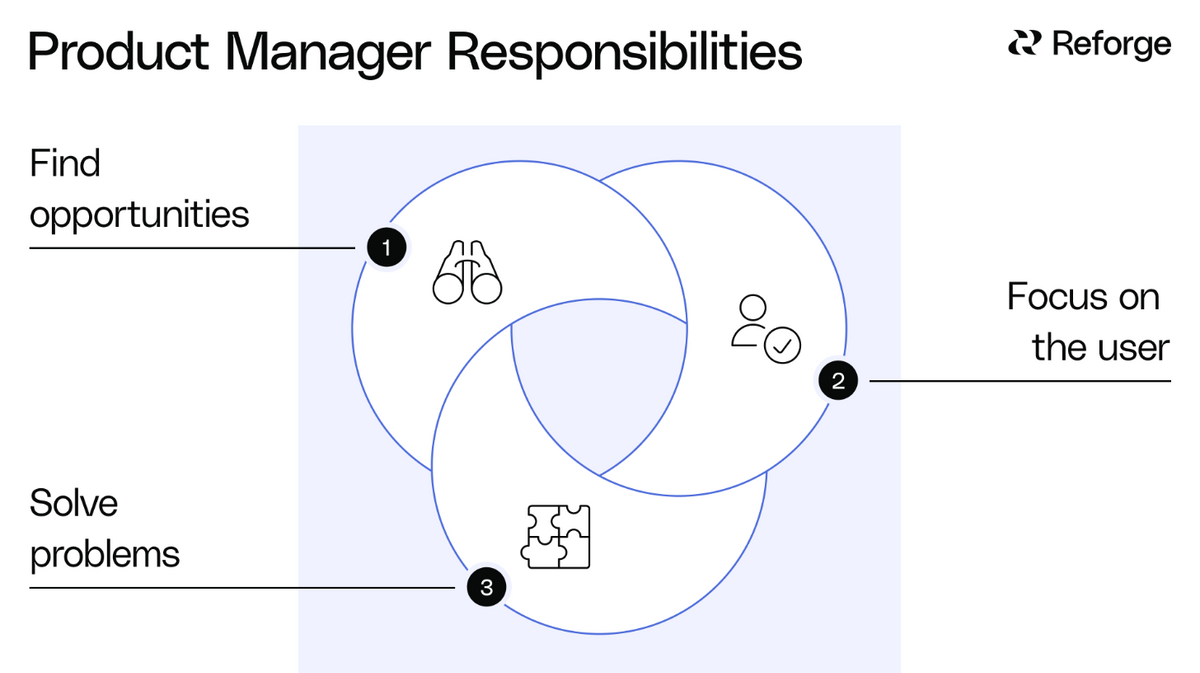
Imagine steering the direction of a product from its inception to its triumphant launch, impacting the lives of countless customers along the way. Product management is a dynamic field that offers immense opportunities to those willing to rise to the challenge. Are you ready to unlock the mysteries of product management and embark on a fulfilling career path?
Let us be your guide to the essentials of product management, the key components of the process, and the vital skills required to thrive in this exciting domain.
Key Takeaways
- Product management is a multifaceted role requiring technical expertise, business acumen and communication skills to guide product strategy.
- Product managers must understand customer needs, prioritize initiatives, collaborate with cross-functional teams and leverage analytics tools for success.
- Aspiring product managers can benefit from gaining foundational knowledge & skills, networking and engaging in professional development opportunities.
The Essence of Product Management
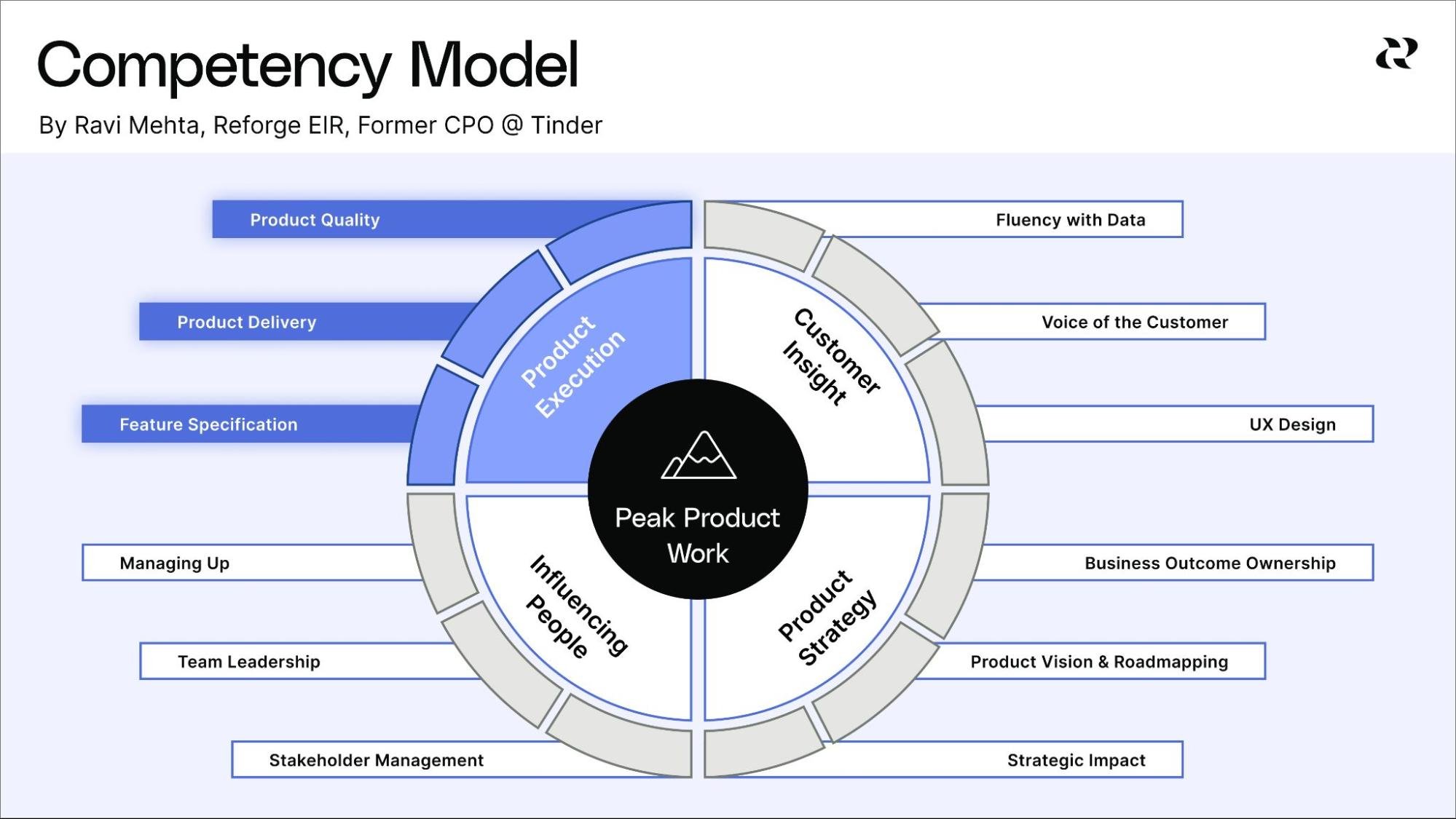
Product management centers around the entire product lifecycle, from ideation to launch and beyond, meeting customer needs while driving business growth. The role of product managers has evolved over time, with the adoption of agile methodologies and customer-centric approaches becoming increasingly important.
Product managers juggle numerous tasks, from market research to roadmap crafting, and collaborate with cross-functional teams to realize product development. To excel in this role, product managers must possess a unique combination of technical expertise, business acumen, and exceptional communication skills, all of which contribute to their ability to guide product strategy, development, and customer value.
Role of a Product Manager
Product managers act as the glue that binds cross-functional teams, guiding product strategy, development, and customer value. A successful product manager must be able to articulate their vision and goals while fostering collaboration among diverse stakeholders such as UX designers, engineers, and marketing teams.
The primary focus of a product manager is not just the efficiency of the team, but the overall success of the product by bridging the gap between business objectives, user experience, and technical capabilities. Engaging with customers is crucial for product managers, as it allows them to gain a deeper understanding of customer needs and refine the product experience accordingly.
Evolution of Product Management
The evolution of product management can be traced back to the Great Depression with the concept of a “brand man” overseeing a particular product rather than a traditional business role.

The expansion of technology companies has led to a surge in demand for knowledgeable product people, paving the way for the growth of product management and its associated roles, such as project managers.
Agile software development has significantly impacted the development of product management, with agile product managers adapting to the fast-paced and iterative nature of agile development. This flexible approach allows for continuous product refinement based on customer data and team reflections, ensuring the product remains relevant and valuable in the ever-changing market landscape.
Key Components of the Product Management Process
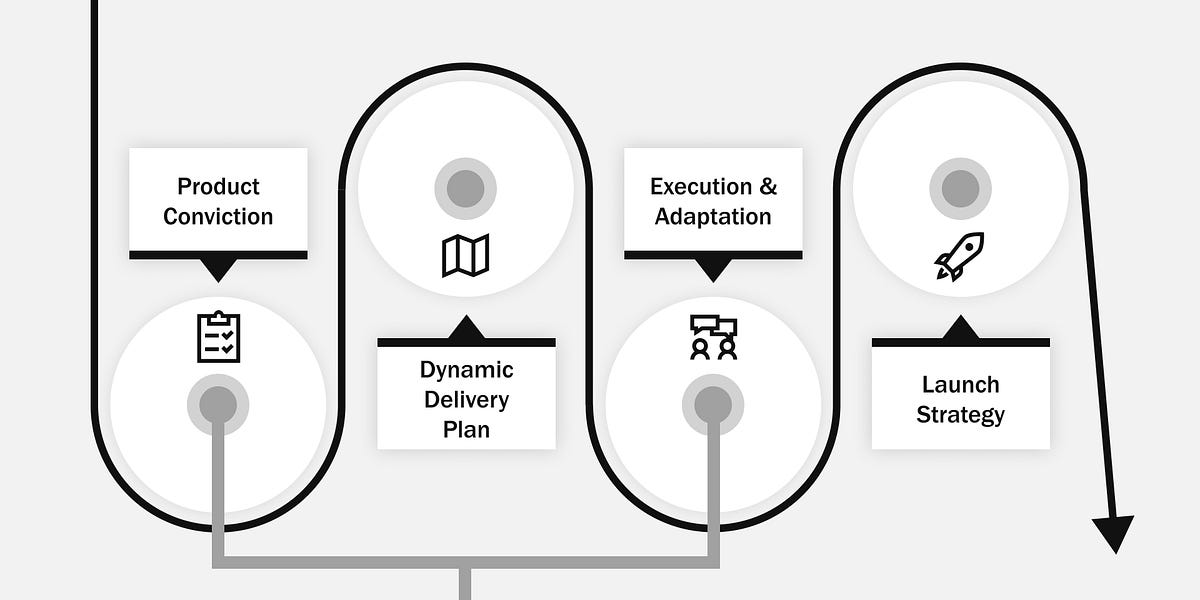
The product management process is a complex dance of several key components, including:
- Identifying customer needs
- Developing a product strategy
- Working with engineering teams
- Crafting a product roadmap
- Executing go-to-market plans
Each of these components plays a vital role in ensuring the product’s success and aligning with overall business objectives.
For any aspiring product manager, mastering these components is key in creating tailored solutions that tackle customer pain points and add value. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into each component, providing insights and guidance on how to excel in the product management process.
Identifying Customer Needs
Understanding and addressing customer needs should be prioritized by product managers to develop solutions that create value. By effectively processing customer feedback, product managers can transform valuable input into actionable ideas, incorporating them into the product roadmap or backlog.
A strong focus on customer needs is the foundation for delivering a product that resonates with the target audience and achieves product-market fit.
Developing a Product Strategy
Creating a product strategy involves setting goals, objectives, and a vision for the product in alignment with overall business objectives. This process includes gathering information, formulating a product strategy, and constructing a product roadmap.
A well-structured product strategy paves a clear path for development execution, ensuring product success.
Product Requirements and Working with Engineering
To define product requirements and assure successful development and execution, product managers collaborate intimately with engineering teams. This collaboration ensures that the product is built to meet customer needs and aligns with the company’s technical capabilities.
Product managers, as part of product management teams, must possess strong technical skills to effectively communicate with the product development team, guiding the product’s development process. In this context, the product team plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless collaboration between product managers and the development team.
Crafting a Product Roadmap
Crafting a product roadmap involves prioritizing features and initiatives, setting timelines, and communicating the plan to stakeholders. The roadmap serves as a visual representation of the product’s development journey, outlining the steps needed to achieve the product vision.
Effective management of the product roadmap helps product managers keep the development process aligned with the overarching product strategy.
Go-to-market and Launch Plans
Go-to-market and launch plans are essential for ensuring a successful product release, as they encompass marketing, sales, and customer support efforts. Product managers must work closely with these teams to create a cohesive launch plan that effectively communicates the product’s value proposition and reaches the target market.
Execution of a well-designed go-to-market strategy can enhance a product’s success chances and spur growth, as steered by product managers through effective product marketing.
Essential Skills for Successful Product Managers
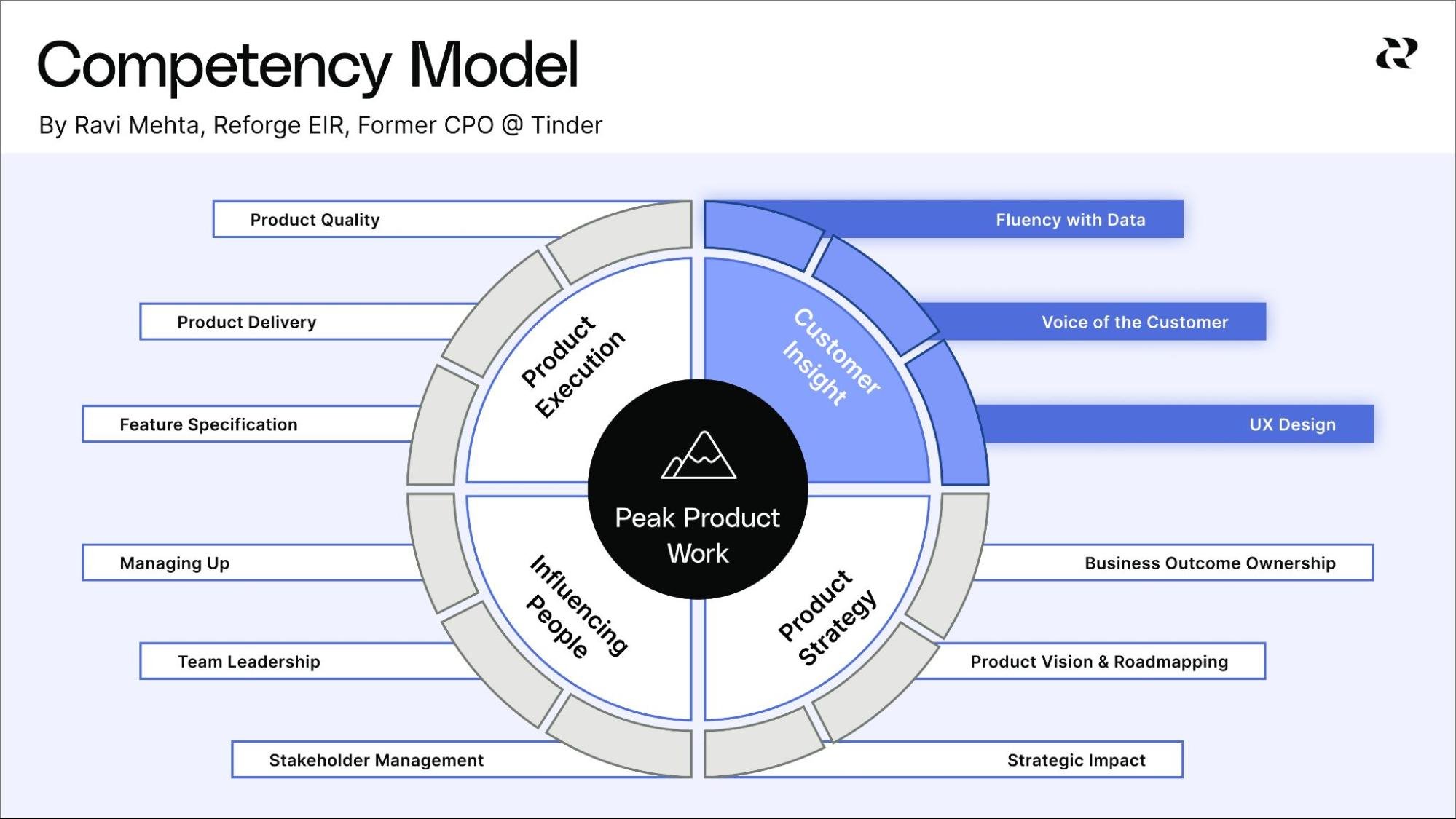
Successful product managers possess a range of essential skills, including strong communication and collaboration abilities, technical expertise, and business acumen. These skills enable product managers to effectively navigate the complex world of product development, working with cross-functional teams and stakeholders to drive product success.
We will delve into each of these crucial skills in the ensuing sections.
Communication and Collaboration
Strong communication and collaboration skills are crucial for product managers to work effectively with cross-functional teams and stakeholders. By effectively articulating their vision and objectives, product managers can foster a collaborative environment that encourages team members to contribute their ideas and expertise.
Additionally, open communication channels enable product managers to receive valuable feedback and insights from stakeholders, allowing them to make informed decisions and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Technical Expertise
Technical expertise allows product managers to:
- Understand the product’s underlying technology
- Work closely with engineering teams
- Guide product development
- Make informed decisions about technical aspects of the product.
As technology continues to advance rapidly, product managers must stay current with emerging trends and best practices to ensure their products remain relevant and competitive in the market.
Business Acumen
Business acumen enables product managers to:
- Make strategic decisions that drive growth and align with overall business objectives
- Understand market trends, customer needs, and competitive landscapes
- Identify opportunities and make informed decisions about product development
This skill is essential for product managers to effectively drive their products forward.
By leveraging their business acumen, product managers can effectively navigate the complex world of product management and drive successful outcomes for their products and organizations.
Navigating Different Product Management Roles
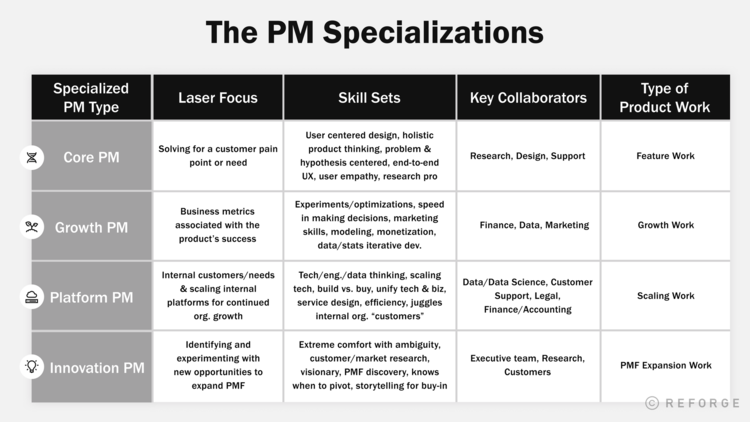
Different product management roles, such as product owner and technical product manager, require varying skill sets and responsibilities, with each role contributing to the overall product strategy and development.
We will further investigate the distinct aspects of each role and their contribution to product success in the sections ahead.
Product Owner
Product owners focus on:
- Managing the product backlog
- Working closely with development teams in an agile environment
- Defining the product vision and strategy
- Prioritizing tasks
- Ensuring that the product delivers value to customers.
As the primary point of contact between the development team and stakeholders, product owners play a crucial role in driving product success and ensuring that customer needs are met.
Technical Product Manager
Technical product managers possess a deep understanding of the product’s technology and work closely with engineering teams to guide development. They are responsible for identifying customer requirements, collaborating with engineering to create the product, and ensuring that the product meets technical standards.
With their technical expertise, technical product managers can effectively bridge the gap between business strategy, customer needs, and technical execution.
Product Manager vs. Product Owner
The roles of product manager and product owner may overlap in some organizations, but each role has distinct responsibilities and focuses. Product managers are responsible for guiding product strategy, development, and customer value, while product owners manage the product backlog and work closely with development teams in an agile setting.
Understanding the differences and overlaps between these roles can help aspiring product managers determine the best path for their career development.
Product Management Careers
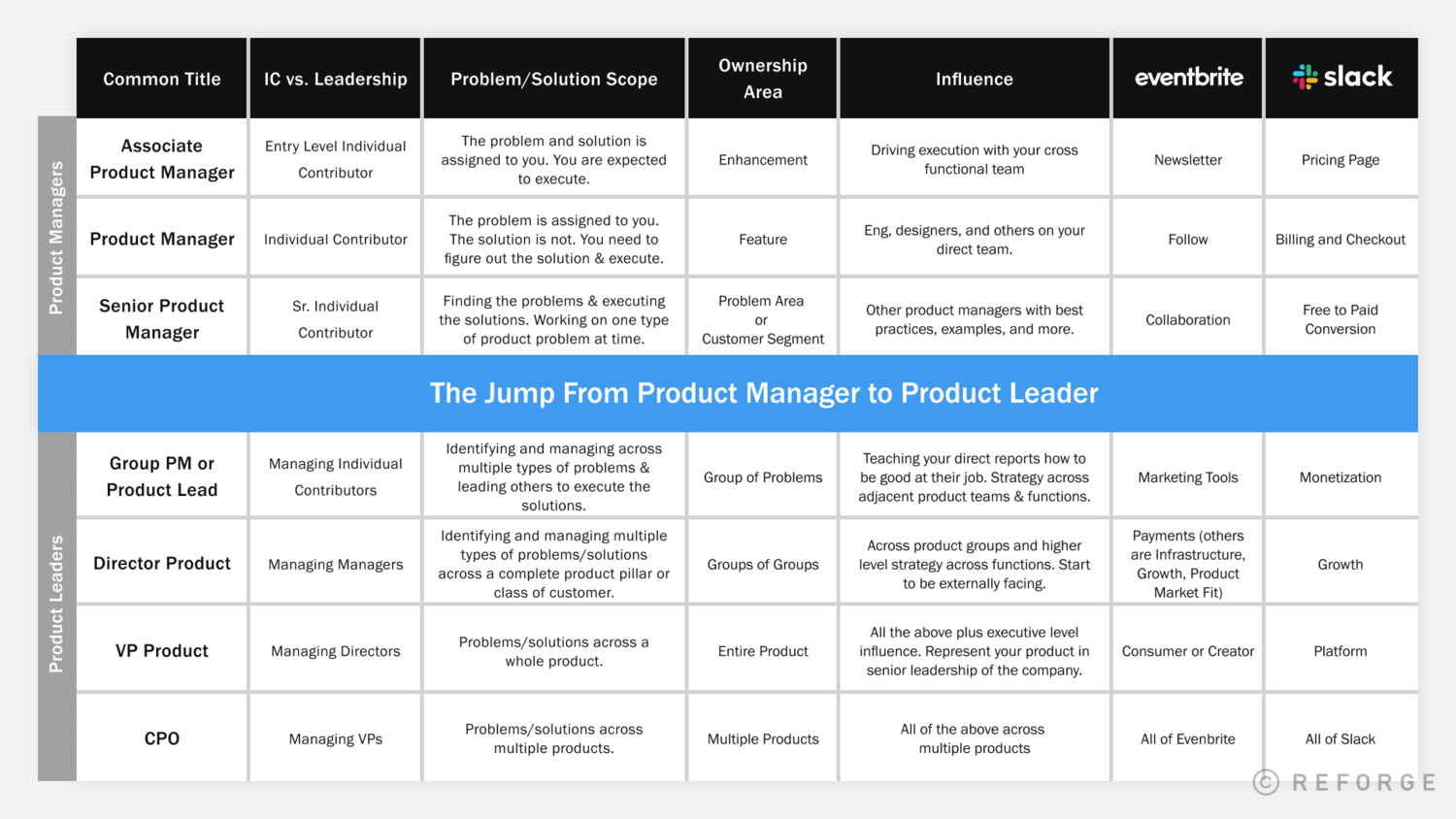
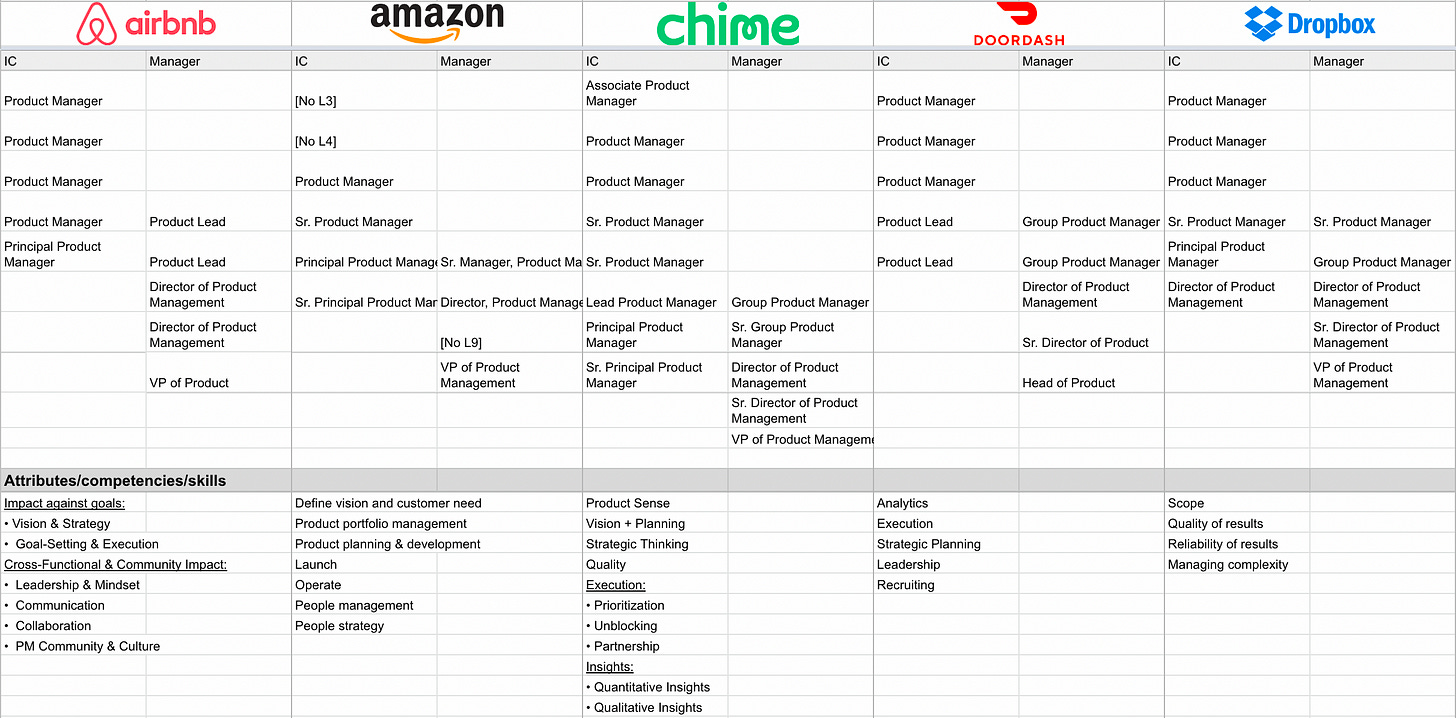
Product management careers span various levels, from entry-level positions to senior roles such as principal product manager, group product manager, VP product, and chief product officer, each with increasing responsibilities and influence.
Titles vary across specialization and company
While the core responsibilities of product management remain relatively consistent, titles can vary significantly depending on the company, industry, and area of specialization. For example, a "Product Manager" at a software company may be called an "Innovation Manager" at a legacy, non-digital enterprise company.
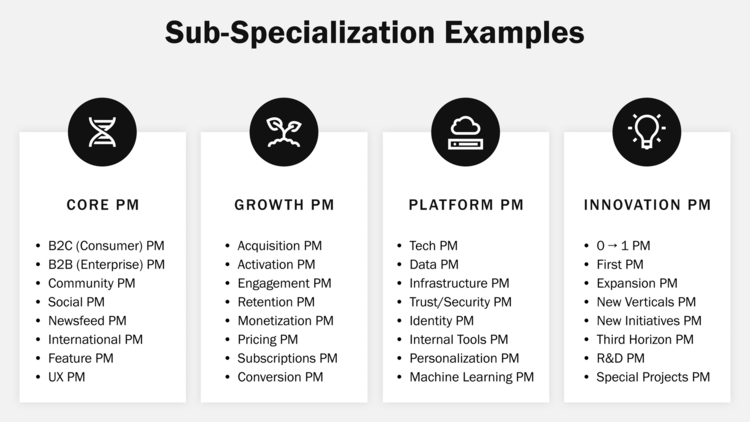
While product managers share common responsibilities across companies, their actual titles and seniority levels can differ significantly depending on the organization. So the levels follow a general progression from junior to director and vice president, but the specific titles depend on the company.
The responsibilities and expectations at each level are generally consistent though, regardless of the exact title.
We will examine the various career levels in product management and their respective unique responsibilities in the sections to come.
Entry Level
At the entry level, product managers are responsible for:
- Assisting in the creation and implementation of product strategies
- Recognizing market opportunities
- Contributing to the overall product roadmap
- Conducting market research
- Analyzing customer feedback
- Working with cross-functional teams to ensure successful product launches.
As they gain experience and hone their skills, entry-level product managers can progress to more senior roles within the product management field. Product management courses and training programs offer a good way to gain broader knowledge and frameworks, but don't replace on-the-job experience.
Senior Product Manager
Senior product managers play a crucial role in driving product strategy, road mapping, and execution across the organization. They are responsible for:
- Developing a cohesive team of product managers and designers
- Ensuring that the company is informed of the product’s vision and direction
- Overseeing product management within the company
With their experience and expertise, senior product managers can guide and mentor junior product managers, helping them grow and develop in their careers.
Principal Product Manager
As a principal product manager, one is responsible for:
- Strategically planning, developing, and launching a company’s products
- Managing the product lifecycle
- Creating strategies
- Defining user stories
- Working on go-to-market strategies for new products.
Additionally, principal product managers may provide coaching and mentorship to other product managers, aiding in their career development.
Group Product Manager
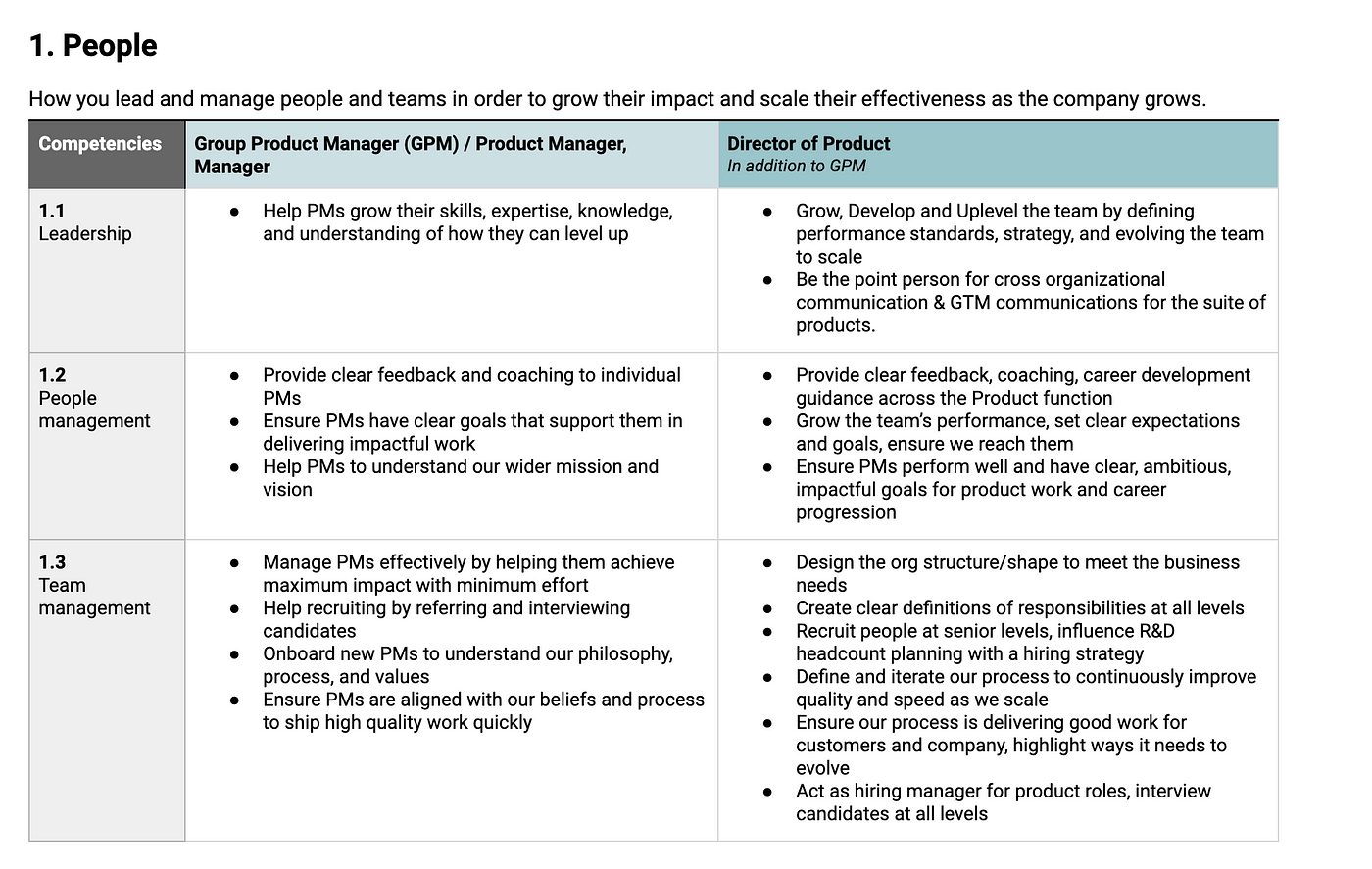
Group product managers oversee the product management of multiple related products within a specific group or team. They are responsible for ensuring that the products under their supervision align with the company’s overall strategy and objectives.
As they gain experience and demonstrate success in managing multiple products, group product managers can advance to higher-level roles within the organization.
VP Product
As head of the product organization, the Vice President of Product is responsible for aligning the product strategy with business goals and overseeing execution across the company. In an organization with a CPO, the VP Product often owns a specific business or product line.
The VP Product plays a pivotal leadership role by:
- Crafting a compelling product vision and leading overall product strategy
- Building a cohesive team of product managers, designers, and researchers
- Guiding the ideation, definition, and development of new products
- Communicating product direction across the organization
- Analyzing market and customer trends to identify opportunities
- Overseeing the product portfolio and making prioritization decisions
- Coaching and mentoring the product management team
- Driving process improvements and optimizing how products are delivered
With a strategic mindset, the VP Product has broad oversight of all product activities. They ensure the organization delivers innovative products that create value for customers and drive business success. The VP Product is a critical driver of the company's product vision and strategy.
Chief Product Officer
As the pinnacle of product leadership, the Chief Product Officer (CPO) is responsible for the strategic direction and success of all products. The CPO oversees the entire product management organization and sets the overall product vision and strategy aligned to company goals.
Key responsibilities include:
- Driving product innovation and experiences that delight customers
- Leading the ideation, development, and launch of new products
- Conducting market analysis to identify growth opportunities
- Promoting collaboration between product, engineering, and design teams
- Evangelizing products internally and externally
- Mentoring and developing PM talent
- Setting standards for product quality and performance
- Optimizing processes to accelerate delivery
With a keen understanding of markets and user needs, the CPO translates business objectives into winning product strategies. As an influential visionary, the CPO plays a crucial role in shaping the company's product direction and customer experiences.
Utilizing Product Management Tools
Product management tools, such as roadmapping and prioritization tools, customer feedback platforms, and analytics software, can help product managers streamline processes, gather insights, and track performance in project management.
We will delve into each of these tools, offering insights on their contribution to a product manager’s success in the subsequent sections.
Roadmapping and Prioritization Tools
Roadmap and prioritization tools assist product managers in planning and organizing product development efforts. By providing a visual representation of the product roadmap, these tools enable product managers to identify and prioritize tasks, track progress, and make adjustments as needed.
Utilizing roadmapping and prioritization tools can help product managers optimize their product development process and ensure that their products remain on track for success.
Customer Feedback and Research Platforms
Customer feedback and research platforms enable product managers to conduct market research and:
- Gather valuable insights
- Understand customer needs
- Identify pain points
- Uncover opportunities for improvement
- Make informed decisions about product development.
Leveraging customer feedback platforms can provide product managers with the insights they need to create products that resonate with their target audience and achieve product-market fit.
Analytics and Performance Tracking Software
Analytics and performance tracking software help product managers in the following ways:
- Monitor product success
- Make data-driven decisions
- Provide insights into user engagement, usage, and performance metrics
- Identify trends
- Uncover insights
- Make informed decisions about product development.
Utilizing analytics and performance tracking software can empower product managers to drive continuous improvement in their products and ensure their success in the market.
Building a Career in Product Management
Building a career in product management involves gaining foundational knowledge and skills, networking, and engaging in professional development opportunities to advance in the field.
We will delve into the steps that aspiring product managers can undertake to foster their careers and attain success in product management in the upcoming sections.
Gaining Foundational Knowledge and Skills
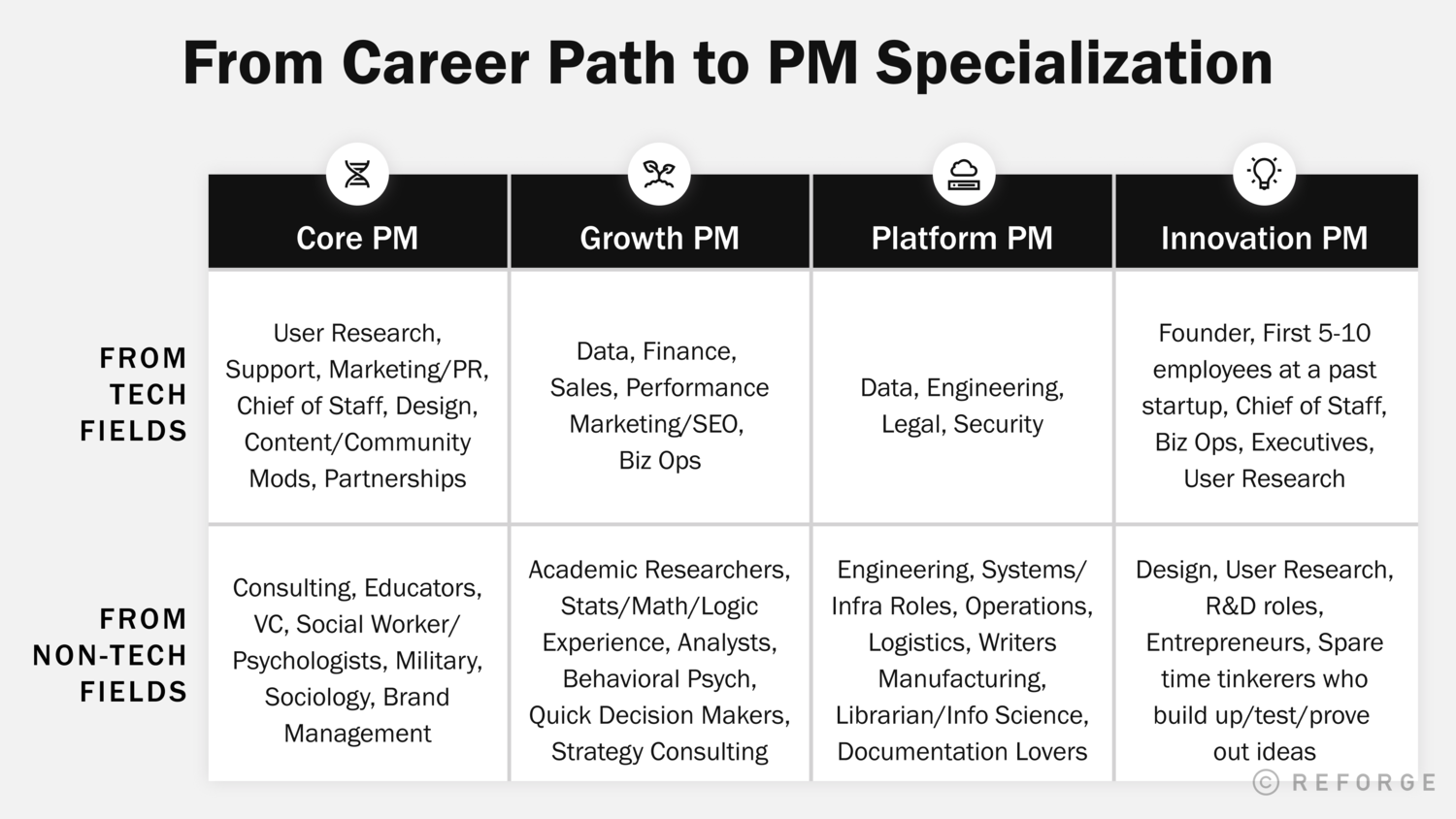
Aspiring product managers should focus on acquiring relevant knowledge and skills, such as understanding product development processes, customer research, and business strategy. By developing a strong foundation in these areas, aspiring product managers can better position themselves for success in the field.
Continuous learning and skill development are crucial for staying up-to-date with industry trends and best practices, ensuring that aspiring product managers remain competitive in the ever-evolving world of product management.
Networking and Professional Development
Networking and professional development opportunities, such as attending industry events and joining online communities, can help aspiring product managers connect with peers and learn from experienced professionals. By actively participating in these events and communities, aspiring product managers can gain valuable insights into the product management field and stay informed of the latest trends and best practices.
Networking can also lead to job opportunities and connections that can further their career growth.
The world of product management offers a wealth of opportunities for those who are willing to rise to the challenge. By understanding the fundamentals of product management, mastering the key components of the process, and developing the essential skills required for success, aspiring product managers can build fulfilling careers in this dynamic field. The journey to becoming a successful product manager may be challenging, but with perseverance and dedication, the rewards can be truly remarkable.
Summary
The multifaceted world of product management offers immense opportunities for growth and impact. By mastering the core components of ideation, strategy, execution, and analysis, aspiring product managers can steer products to success.
Start by understanding customer pain points, honing collaboration abilities, and developing business acumen.
Keep learning through networking, mentorships, and professional development.
Stay up-to-date on the latest industry trends and best practices.
With the right mindset and skillset, you can craft brilliant products that deliver real value to customers. The journey requires perseverance, but the rewards are plentiful.
Seize this exciting chance to combine creativity, strategy, and leadership. Embark on your product management career today and unlock your full potential to thrive in this dynamic field.
The future is yours to shape - now go build it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a product manager do?
Product Managers are responsible for defining customer needs and product vision, overseeing the development of a product or feature, liaising between teams, researching customer data and market trends, and ensuring the success of the product in terms of customer satisfaction and return on investment.
They must have a deep understanding of the customer, the market, and the product. They must be able to identify customer needs and develop a product vision that meets those needs. They must also be able to collaborate with other teams to ensure the product is developed and launched successfully.
Product Managers must also be able to analyze customer data.
What are the 3 major areas of product management?
Product Management involves three key areas: Product Discovery, Planning and Development. These three areas focus on the end-to-end process of bringing a product to market.
Product Discovery involves researching customer needs and market trends to identify potential opportunities. Planning involves creating a product roadmap and setting goals for the product. Development involves designing.
What is product management in simple terms?
Product Management is the process of guiding a product from its development and launch to positioning and pricing with customer satisfaction in focus. It typically falls within the product development department and covers all aspects of a product’s lifecycle.
How has the agile methodology impacted the field of product management?
Agile methodology has allowed product managers to stay abreast of fast-paced development and make timely decisions, resulting in improved product success.
What are the essential skills required for successful product managers?
Successful product managers need a combination of hard and soft skills to excel in their roles. The essential skills for successful product managers include:
- Critical Thinking and Analytical Skills: These are essential for analyzing data, making informed decisions, and solving complex problems.
- Understanding of Web Development: A basic understanding of web development can help product managers communicate more effectively with their technical teams and understand the possibilities and limitations of their products.
- Agile Methodology Knowledge: Familiarity with Agile methodologies can help product managers work more effectively within their teams and adapt to changes quickly.
- Product Research: This skill involves understanding market trends, customer needs, and competitive landscapes to inform product development.
- Prototyping: This involves creating early models of products to test and refine concepts.
- A/B Testing: This involves testing two versions of a product feature to see which one performs better.
- Data Analysis: This involves interpreting complex data to make informed decisions about product development and improvements.
- Prioritization and Roadmapping: These skills involve deciding what features to build and when, and planning the development of a product over time.
- Communication Skills: Product managers need to effectively communicate with different stakeholders, including their teams, executives, and customers.
- Collaboration and Cross-Functional Teamwork: Product managers often work with diverse teams and need to collaborate effectively to get things done.
- Technical Expertise: A deep understanding of the technology behind their products can help product managers make more informed decisions.
- Business Skills: These include understanding business strategies, marketing, and financial planning.
- Research Skills: These involve gathering and interpreting information about markets, customers, and competitors.
- Leadership Skills: Product managers often lead teams and need to inspire and motivate others.
- Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others, particularly customers, can inform product development.
- Flexibility: Product managers need to adapt to changes and be open to new ideas.
- Problem-Solving Skills: These involve finding solutions to challenges in product development.
- Time Management Skills: Product managers need to manage their own time and the time of their teams effectively.
These skills enable product managers to analyze information, develop and design products, lead product teams, and efficiently navigate the product life cycle. Additionally, product managers should be open to learning about new technologies and Agile methodologies to stay competitive and effective in their roles.
